What’s the Average Student Loan Interest Rate?
Student loans, like any loans, have an interest rate. While interest rate accrual on existing federal student loans was paused for more than three years due to the Covid-19 forbearance, interest accrual resumed on September 1, 2023, and payments resumed in October 2023. And of course, any new student loans — federal or private — will have an interest rate that impacts the total cost of the loan.
So what is the average student loan interest rate? In this guide, we’ll look at the interest rates of new federal student loans, as well as the range of rates for private student loans.
Table of Contents
- What Is The Average Student Loan Interest Rate?
- How Student Loan Interest Is Calculated and Applied
- How to Evaluate Student Loan Interest Rates
- Average Interest Rates for Student Loans FAQ
- What Is a Good Fixed Interest Rate for Student Loans?
- Ways to Lower Your Student Loan Interest Rate
- Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates: Which Is Better?
Key Points
• Federal student loan interest rates for 2024-25 are 6.53% for undergraduates, 8.08% for graduate students, and 9.08% for PLUS loans.
• Private student loan interest rates range from 3.50% to 17.00% as of March 2025.
• Federal interest rates are fixed rates that are set annually using formulas tied to the 10-year Treasury note and a statutory add-on percentage.
• Lenders set their own rates for private student loans. The interest rate on these loans may be fixed or variable.
• Interest rates for federal loans have increased from the previous year, while private loans have a wide range of rates influenced by market conditions.
What Is The Average Student Loan Interest Rate?
The interest rate on a student loan varies based on the type of student loan. Federal student loans issued after July 1, 2006, have a fixed interest rate. The rates on newly disbursed federal student loans are determined annually by formulas specified in the Higher Education Act of 1965 (HEA).
These are the federal student loan interest rates for the 2024–25 school year:
• 6.53% for Direct Subsidized or Unsubsidized loans for undergraduates
• 8.08% for Direct Unsubsidized loans for graduate and professional students
• 9.08% for Direct PLUS loans for graduate students, professional students, and parents
All three of those rates have risen from the 2023-2024 school year, and the undergraduate rate has more than doubled since the 2020-2021 school year.
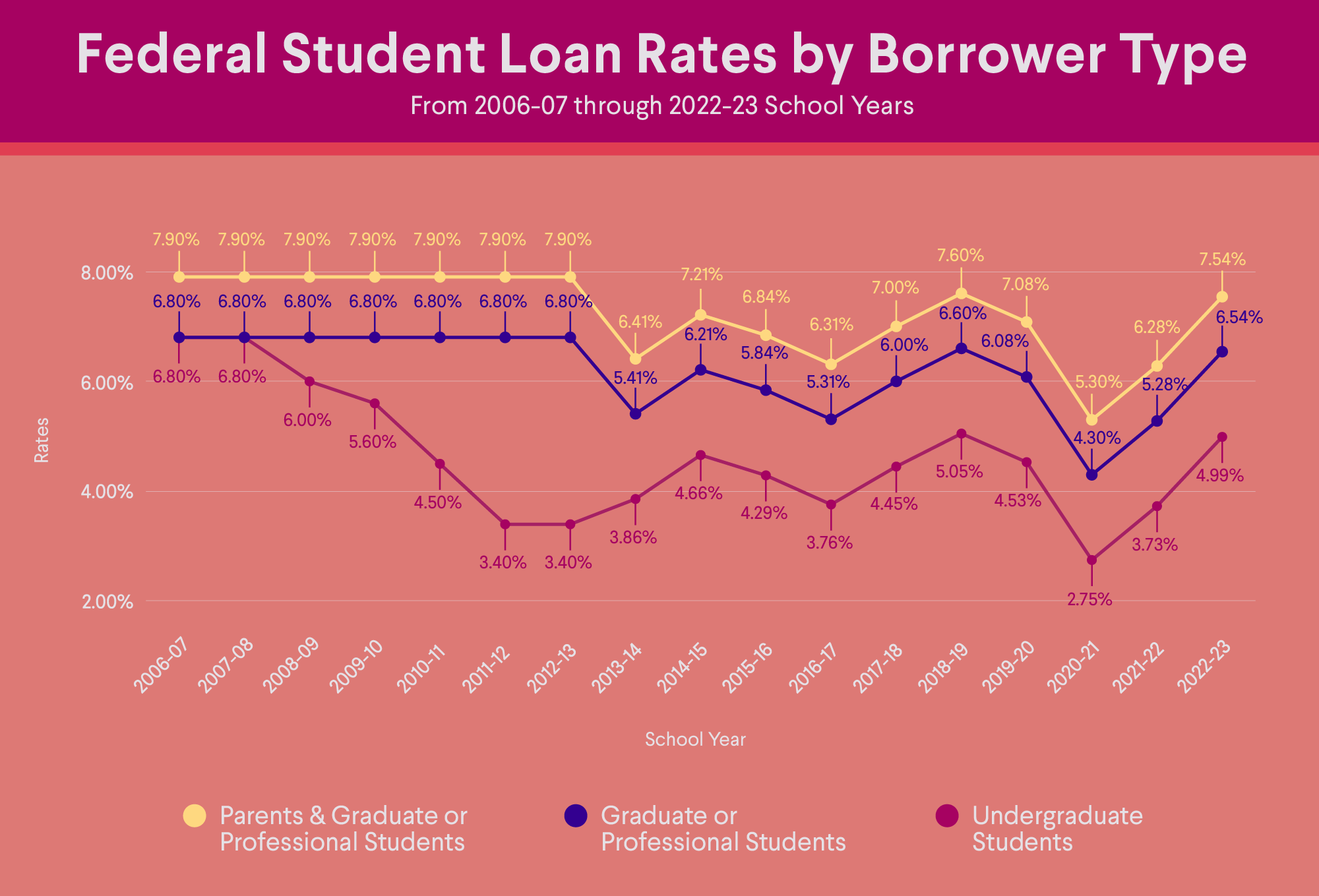
Source: Studentaid.gov
This means that the average student loan interest rate for the three main types of federal student loans is 7.89%.
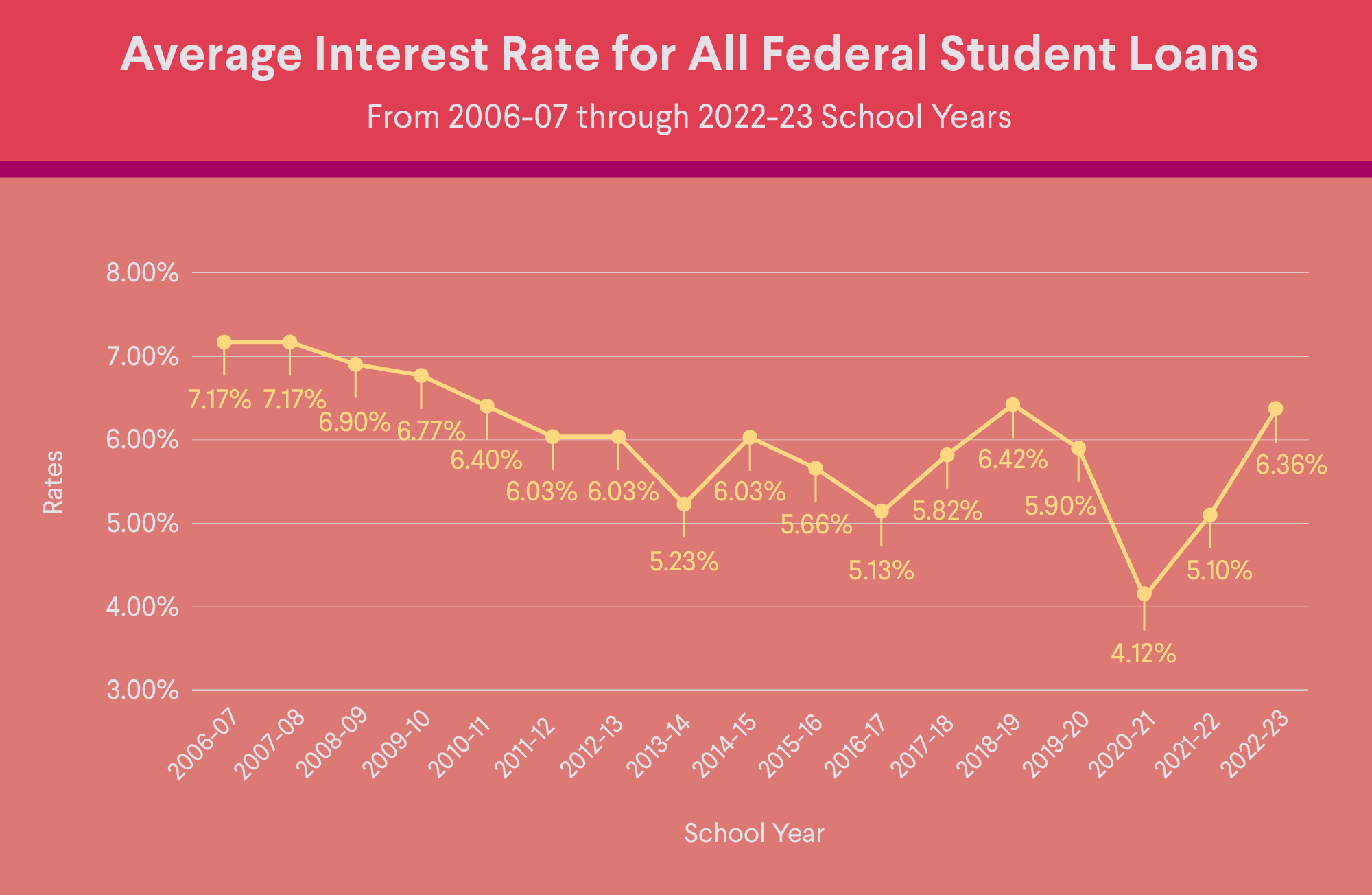
Source: Studentaid.gov
Private student loan interest rates vary by lender and each has its own criteria for which rates borrowers qualify for. Private student loans can have either fixed interest rates that remain the same over the life of the loan, or variable rates that may start lower than a fixed interest rate but then go up over time, based on market changes.
Private loans require a credit check, and lenders may offer different interest rates if you have strong credit or a cosigner on your student loan. The interest rates on private student loans can vary anywhere from 3.50% to 17.00% (as of March 2025), depending on the lender, the type of loan, and on individual financial factors including the borrower’s credit history.
Recommended: Do Student Loans Have Simple or Compound Interest?
How Are Interest Rates Determined?
As mentioned, the interest rates on federal student loans are set annually by formulas specified in the HEA. The rates are tied to the financial markets — federal law sets them based on the 10-year Treasury note and a statutory add-on percentage with a maximum rate cap.
Since July 2006, all federal student loans have fixed interest rates. Although federal student loans are serviced by private companies or nonprofits selected by the federal government, these loan servicers have no say in the federal interest rate offered.
For private student loans, the lenders set their own rates, though they often take cues from federal rates. The rates quoted for student loans vary based on each applicant’s individual situation — though generally the better a potential borrower’s credit history is, the better rate they may be able to qualify for.
To learn more about private and federal student loans, check out our student loan help center.
How Student Loan Interest is Calculated and Applied
Interest on federal student loans typically accrues daily. To calculate the interest as it accrues, the following formula can be used:
| Interest amount = (outstanding student loan principal balance × interest rate factor) × days since last payment |
In other words, you will multiply your outstanding loan balance by the interest rate factor, which is used to calculate the amount of interest that accrues on a student loan. Then, multiply that result by the days since you last made a payment.
To calculate the interest rate factor you can divide the interest rate by the number of days of the year (365). For example, let’s say you have an outstanding student loan balance of $10,000, an interest rate of 4.75%, and it’s been 30 days since your last payment. Here’s how to calculate your interest:
| $10,000 x (4.75%/365) = $1.30 daily interest charge |
| $1.30 x 30 days = $39 |
| Interest amount $39 |
Many private student loans will also accrue interest on a daily basis; however, the terms will ultimately be determined by the lender. Review the lending agreement to confirm.
Recommended: Do Student Loans Count as Income?
How to Evaluate Student Loan Interest Rates
When you take out a federal student loan, you’ll receive a fixed interest rate. This means that you’ll pay a set amount for the term of the student loan. In addition, all of the terms, conditions, and benefits are determined by the government. Federal student loans also provide some additional perks that you may not find with private lenders, like deferment.
Private student loans can have higher interest rates and potentially fewer perks than federal student loans. You may want to take advantage of all federal student loans you qualify for before comparing private loan options.
One thing to keep in mind is that interest you pay on student loans may allow you to take the student loan interest deduction on your taxes.
What Is a Good Fixed Interest Rate for Student Loans?
The lower the interest rate, the less a borrower will owe over the life of the loan, which could help individuals as they work on other financial goals. If you’re taking out federal loans, the student loan interest rate is set by federal law, so you don’t have a choice for what is and isn’t a reasonable interest rate.
When it comes to private student loans, it’s wise to shop around and compare your options to find the most suitable financing solution. Since every lender offers different terms, rates, and fees, getting quotes from multiple lenders may help you select the best option for your personal needs. Keep in mind that the rate you receive on a private student loan is largely dependent on your credit score and other factors, whereas federal student loan interest rates are based on HEA formulas.
Also keep in mind that private student loans do not have the same borrower protections as federal student loans, including deferment options, and should be considered only after all federal aid options have been exhausted.
Ways to Lower Your Student Loan Interest Rate
The interest rate on federal student loans, while fixed for the life of the loan, does fluctuate over time. For example, the rates for Direct Subsidized and Unsubsidized loans for undergraduates more than doubled from 2.75% in 2020–21 to 6.53% in 2024–25.
To adjust the rate on an existing student loan, borrowers generally have two options. They can refinance student loans or consolidate them with hopes of qualifying for a lower interest rate.
Refinancing a federal loan with a private lender eliminates them from federal borrower protections such as federal deferment or Public Service Loan Forgiveness. The federal government does offer a Direct Consolidation Loan, which allows borrowers to consolidate their federal loans into a single loan. This will maintain the federal borrower protections but won’t necessarily lower the interest rate. When federal loans are consolidated into a Direct Consolidation Loan, the new interest rate is a weighted average of your original federal student loans’ rates.
Refinancing student loans with a private lender may allow qualifying borrowers to secure a lower interest rate or preferable loan terms. Note that extending the repayment term will generally result in an increased cost over the life of the loan.
To see how refinancing could work for your student loans, try this student loan refinance calculator.
💡 Quick Tip: Refinancing comes with a lot of specific terms. If you want a quick refresher, the Student Loan Refinancing Glossary can help you understand the essentials.
Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates: Which Is Better?
Whether fixed or variable interest rates are better depends on a borrower’s specific situation. For many borrowers, fixed rates are often a better option because they are stable and predictable. Your payments won’t change, and you won’t have to worry about rate hikes. Borrowers may want to consider a student loan with a fixed interest rate if interest rates are rising overall and they anticipate needing a number of years to repay their loan.
Because variable interest rates fluctuate with the market, they can be unpredictable. That means your payments can potentially change from one month to the next.
The Takeaway
The average student loan interest rate varies depending on the loan type. The interest rate for federal Direct Unsubsidized and Subsidized loans is set annually by federal law and fixed for the life of the loan.
The interest rate on private student loans is determined by a variety of factors including the borrower’s credit history and may range anywhere from 3.50% to to 17%.
Looking to lower your monthly student loan payment? Refinancing may be one way to do it — by extending your loan term, getting a lower interest rate than what you currently have, or both. (Please note that refinancing federal loans makes them ineligible for federal forgiveness and protections. Also, lengthening your loan term may mean paying more in interest over the life of the loan.) SoFi student loan refinancing offers flexible terms that fit your budget.
FAQ
How often do student loan interest rates change?
The rates on federal student loans are determined and set annually by formulas specified in the Higher Education Act of 1965. Private student loan rates vary by lender, and they may be fixed or variable. Private loans with variable rates can change based on market changes.
How do federal student loan interest rates compare to private loans?
The interest rate on federal student loans is often lower than the rates for private student loans. The rate you may qualify for with a private loan depends on your circumstances. If you have strong credit or a loan cosigner who has strong credit, you may be able to get a loan with a lower interest rate.
Keep in mind that federal student loans have fixed interest rates, which means the interest and your monthly payment won’t change. Private student loans may have fixed or variable rates, and variable rates can go up or down with market changes.
Can I negotiate my student loan interest rate?
Federal student loans have fixed rates that are non-negotiable. With a private student loan, it’s possible that you may be able to negotiate the interest rate, especially if you are struggling to make payments or dealing with financial hardship. Call your private lender and explain the situation.
What factors determine my student loan interest rate?
Federal student loans have a fixed interest rate that is determined and set each year based on formulas specified in the Higher Education Act of 1965. With private student loans, each lender sets their own rates. Private loans require a credit check, and the interest rates vary based on an applicant’s credit and other factors. Generally speaking, the stronger a borrower’s credit is (or if they have a loan cosigner with strong credit), the lower the rate they may be able to qualify for.
Is it better to choose a fixed or variable interest rate for student loans?
For many borrowers, fixed rates may be a better option because they are stable and predictable, which means the monthly payments won’t change over the life of the loan. If you are planning to repay your loan over a period of years, you may want to consider a student loan with a fixed interest rate.
Variable interest rates fluctuate with the market, which makes them unpredictable. As a result, your payments can go up (or down), and may be harder to budget for.
About the author
SoFi Student Loan Refinance
Terms and conditions apply. SoFi Refinance Student Loans are private loans. When you refinance federal loans with a SoFi loan, YOU FORFEIT YOUR ELIGIBILITY FOR ALL FEDERAL LOAN BENEFITS, including all flexible federal repayment and forgiveness options that are or may become available to federal student loan borrowers including, but not limited to: Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF), Income-Based Repayment, Income-Contingent Repayment, extended repayment plans, PAYE or SAVE. Lowest rates reserved for the most creditworthy borrowers. Learn more at SoFi.com/eligibility. SoFi Refinance Student Loans are originated by SoFi Bank, N.A. Member FDIC. NMLS #696891 (www.nmlsconsumeraccess.org).
SoFi Loan Products
SoFi loans are originated by SoFi Bank, N.A., NMLS #696891 (Member FDIC). For additional product-specific legal and licensing information, see SoFi.com/legal. Equal Housing Lender.
Third-Party Brand Mentions: No brands, products, or companies mentioned are affiliated with SoFi, nor do they endorse or sponsor this article. Third-party trademarks referenced herein are property of their respective owners.
Non affiliation: SoFi isn’t affiliated with any of the companies highlighted in this article.
Tax Information: This article provides general background information only and is not intended to serve as legal or tax advice or as a substitute for legal counsel. You should consult your own attorney and/or tax advisor if you have a question requiring legal or tax advice.
Disclaimer: Many factors affect your credit scores and the interest rates you may receive. SoFi is not a Credit Repair Organization as defined under federal or state law, including the Credit Repair Organizations Act. SoFi does not provide “credit repair” services or advice or assistance regarding “rebuilding” or “improving” your credit record, credit history, or credit rating. For details, see the FTC’s website .
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
External Websites: The information and analysis provided through hyperlinks to third-party websites, while believed to be accurate, cannot be guaranteed by SoFi. Links are provided for informational purposes and should not be viewed as an endorsement.
SOSLR-Q125-025
Read more




