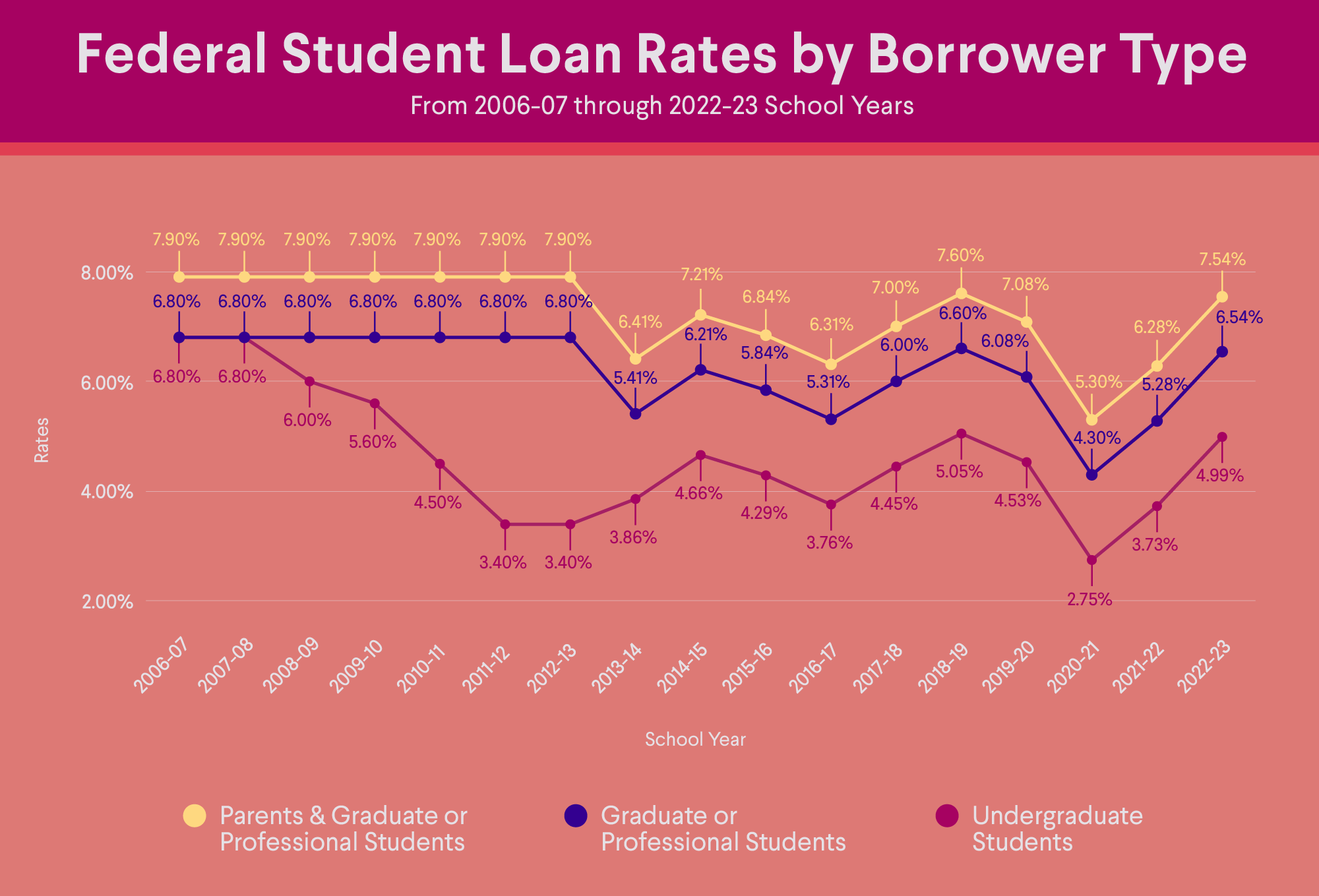
Smart Strategies to Lower Your Student Loan Payments
Staying on top of student loan payments is an important part of your overall financial health. If you’re concerned about making payments on time, or if you’re reevaluating your budget, you may be wondering how to lower student loan payments.
Many borrowers may be eligible for options that can reduce their student loan payments. Read on to learn about some strategies that could help.
Key Points
• Borrowers struggling to pay student loans have several options for reducing their monthly payments.
• Enrolling in autopay can reduce the student loan interest rate by 0.25%, helping to make monthly payments more manageable.
• Federal student loan repayment plans like the Graduated Repayment Plan and the Extended Repayment Plan can lower monthly payments but increase total interest paid.
• Loan assistance and forgiveness programs might help reduce or eliminate student loan debt for some borrowers.
• Refinancing private student loans can potentially lower interest rates and result in more favorable loan terms for those who qualify.
Can You Reduce Your Student Loan Payments?
There are several ways you may be able to lower your monthly payments. For example, if you have federal student loans, the Graduated Repayment Plan, in which your payments start small and gradually go up over time, is an option you can explore.
Borrowers might also want to consider refinancing student loans at a lower interest rate or with a longer loan term, both which may lower monthly payments. (Note: You may pay more interest over the life of the loan if you refinance with an extended term.) It’s possible to refinance private and federal student loans, although there are many factors to consider.
Assessing Your Student Loan Repayment Situation
Before you can determine if you can lower your student loan payments, however, it’s important to know the type of loans you have, since this can affect your student loan repayment options.
You can find all of your federal student loans and the individual loan servicers, by logging into your account on Federal Student Aid.
Unless you choose another plan, federal loans are automatically placed in the Standard Repayment Plan, which sets your monthly payments at a fixed amount so your loans will be paid off within 10 years. Some private loans also follow the 10-year repayment timeline, but it varies depending on the lender.
The next step is to assess how much debt you have in total. By calculating what you owe, you can get a better understanding of how your current repayment plan is working and whether you want to consider changing it.
Once you have all of your loan information, you can use a student loan payoff calculator or contact your loan servicer to find your current payoff dates for your student loans. The calculator can also help you determine which repayment plans you qualify for. Keep in mind that if you change to a longer term to lower your monthly student loan payments, you may end up paying more over the life of the loan since interest will continue to accumulate over the longer term.
If you only need temporary relief, consider contacting your loan servicer to see if you are eligible for student loan deferment or forbearance. Both options let borrowers temporarily pause or lower loan payments for reasons such as unemployment or going back to school. Depending on the type of loan you have, interest may still accrue during this time.
Recommended: When Do You Have to Start Paying Back Student Loans?
Ways to Lower Your Monthly Student Loan Payments
There are different ways to reduce your student loan payments. One or more of these methods might be right for your situation.
1. Enroll in Autopay for Interest Rate Reductions
Federal loan servicers and some private lenders offer incentives if you elect to make automatic payments, such as a 0.25% interest rate reduction. With auto payments, you won’t have to worry about missing student loan due dates. Autopay can also help you incorporate your student loan payments into your budget as an expense that must be accounted for every month.
2. Talk to Your Loan Servicer About Alternative Repayment Plan Options
If you’re interested in changing federal repayment plans to help lower student loan payments, contact your loan servicer to learn more.
One option is the Graduated Repayment Plan, as mentioned, which has a payment timeline of 10 years (or up to 30 years for Direct Consolidation loans), and starts out with lower monthly payments. The payment amount gradually increases, usually every two years. Note that you will likely pay more in interest with this plan.
If you have more than $30,000 in eligible outstanding student debt on most loans, you can also ask about the Extended Repayment Plan, which lengthens your loan repayment timeline to 25 years and can make your monthly payments smaller. However, you may end up paying more in interest over the life of the loan on the extended plan.
3. Consider Income-Driven Repayment for Federal Loans When Available
As of March 2025, access to income-driven (IDR) plans for new borrowers is currently on hold while the Trump administration reevaluates these plans. You can find out more about this and any new developments on the Federal Student Aid website. In the meantime, here is a quick rundown of how these plans typically work.
On an IDR plan, how much you owe each month is based on your monthly discretionary income and family size. IDR options typically offer loan forgiveness after borrowers make consistent payments for a certain number of years. However, forgiveness on all but one of the IDR plans is currently paused.
These are the types of IDR plans.
• Income-Based: Payments are generally about 10% of a borrower’s discretionary income, and any outstanding balance is forgiven after 20 or 25 years.
Note that on the IBR plan, forgiveness after the repayment term has been met is still proceeding as of March 2025, since this plan was separately enacted by Congress.
• Saving on a Valuable Education (SAVE): As of March 2025, the SAVE plan is no longer available after being blocked by a federal court. Forgiveness has been paused for borrowers who were already enrolled in the plan and they have been placed in interest-free forbearance.
• Pay As You Earn (PAYE): A borrower’s monthly payment on PAYE is roughly 10% of their discretionary income, and they’ll make 20 years of payments. As of March 2025, forgiveness has been paused for borrowers who were already enrolled in the plan, and they have been placed in interest-free forbearance.
• Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR): The monthly payment amount on this plan is either 20% of a borrower’s discretionary income divided by 12, or the amount they would pay on a repayment plan with a fixed payment over 12 years, whichever is less. The repayment term is 25 years. As of March 2025, forgiveness has been paused for borrowers who were already enrolled in the plan and they have been placed in interest-free forbearance.
4. Explore Loan Assistance and Forgiveness Programs
If you’re eligible, a Loan Repayment Assistance Program (LRAP) can provide funds to help you lower your student loan payments. Since private loans are not eligible for the federal income-based repayment plans mentioned above, an LRAP could be helpful for those with both private and federal student loans.
Some states, organizations, and companies may offer LRAPs, especially if you work in certain fields like health care or education. LRAPs often include a requirement that you work in your eligible job for a certain number of years, typically in public service.
There are also federal and state forgiveness programs you may be eligible for. For example, if you have federal student loans and you’re employed by government entities or nonprofits, you might qualify for Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF). Borrowers pursuing this program agree to work in underserved areas and must meet specific requirements to have their loan forgiven after 120 qualifying payments on an income-driven repayment plan.
A number of states also have student loan forgiveness programs, especially for individuals working in health care and education. Check with your state’s department of education to see what’s available.
5. Refinance to Potentially Lower Interest Rates
Student loan refinancing is an option that may be helpful if you have student loans with high interest rates or private student loans.
When you refinance student loans, a lender pays off your existing loans and gives you a new loan with new terms. Refinancing may save you money in the long run if you get a lower interest rate, or you could change your term to get more time to pay off your loan and lower the cost of your monthly student loan payments, though you may pay more in interest in the long run.
Keep in mind, however, that if you refinance a federal student loan, you’ll lose access to federal benefits and protections.
What to Do if You Can’t Afford Your Student Loan Payments
With most federal student loans, if you don’t make a payment in more than 270 days, you’ll default on the loan. Private loans are often placed in default as soon as after 90 days.
Defaulting can impact your credit score, and have other negative consequences, including losing eligibility for deferment, forbearance, and other valuable repayment options. The best path forward is to avoid default. If you are having trouble making payments, contact your loan servicer right away.
Planning for Life After Student Loan Repayment
Along with managing your student loan payments, it’s also important to save for your future. That might include a down payment on a house, putting money away for your child’s education, and investing for retirement.
To plan for life after student loan repayment, work to build an emergency fund to handle sudden expenses, such as medical bills or job loss. Aim to have at least three to six months’ worth of expenses in your emergency fund, and keep it in a separate bank account so you won’t be tempted to spend it.
Also, open a savings account, if you don’t already have one, to put away money each week or month for your financial goals. Participate in your 401(k) at work, if that’s an option. And you might also want to consider opening an IRA to help maximize your retirement savings and secure your financial future.
Refinancing Student Loans With SoFi
There are several strategies to make your student loan payments more manageable, including choosing a new repayment plan, signing up for autopay, and student loan refinancing. Explore the options to determine what makes sense for your situation.
Looking to lower your monthly student loan payment? Refinancing may be one way to do it — by extending your loan term, getting a lower interest rate than what you currently have, or both. (Please note that refinancing federal loans makes them ineligible for federal forgiveness and protections. Also, lengthening your loan term may mean paying more in interest over the life of the loan.) SoFi student loan refinancing offers flexible terms that fit your budget.
FAQ
Can you negotiate student loans down?
You generally can’t negotiate student loans unless you’ve stopped making payments and your loans are delinquent or in default, a situation that has serious financial consequences, such as potentially damaging your credit score.
There are other options to lower student loan payments, however. If you need temporary relief, you can contact your loan servicer to see if you’re eligible for deferment or forbearance. If you have federal loans, you may be able to change your loan term or enroll in a different repayment plan. Borrowers with private loans can explore refinancing their student loans to see if they qualify for a lower interest rate or more favorable loan terms.
How do I negotiate student loan payoff?
If your student loans are delinquent or in default, you may be able to negotiate a settlement for a lower payment amount, but this is generally seen as a last resort because of the negative financial consequences. If you are struggling to make your payments, contact your lender to see what other options may be available to you.
What is average student loan debt?
The average student borrower has $38,375 in student loans to pay off, according to the Education Data Initiative.
What are the pros and cons of refinancing student loans?
The pros of student loan refinancing include potentially getting a lower interest rate on your loan or better loan terms if you qualify. Your loans may also be easier to manage because you can streamline them into one new loan with one monthly payment.
The disadvantages of student loan refinancing include potentially paying more in interest if you lengthen your repayment term to lower your monthly payments and losing access to federal benefits if you refinance federal loans. Weigh the pros and cons to decide if refinancing makes sense for you.
Does deferment or forbearance affect my credit score?
Neither deferment nor forbearance affect your credit score. Both options allow you to temporarily stop payments on your student loans if you are struggling to afford them. The main difference between them is that with deferment, some federal student borrowers may not be required to pay the interest that accrues on certain types of loans during the deferment period. With forbearance, a borrower is generally required to cover accruing interest while the loan is in forbearance.
SoFi Student Loan Refinance SoFi Loan Products
Terms and conditions apply. SoFi Refinance Student Loans are private loans. When you refinance federal loans with a SoFi loan, YOU FORFEIT YOUR ELIGIBILITY FOR ALL FEDERAL LOAN BENEFITS, including all flexible federal repayment and forgiveness options that are or may become available to federal student loan borrowers including, but not limited to: Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF), Income-Based Repayment, Income-Contingent Repayment, extended repayment plans, PAYE or SAVE. Lowest rates reserved for the most creditworthy borrowers. Learn more at SoFi.com/eligibility. SoFi Refinance Student Loans are originated by SoFi Bank, N.A. Member FDIC. NMLS #696891 (www.nmlsconsumeraccess.org).
SoFi loans are originated by SoFi Bank, N.A., NMLS #696891 (Member FDIC). For additional product-specific legal and licensing information, see SoFi.com/legal. Equal Housing Lender.
Third-Party Brand Mentions: No brands, products, or companies mentioned are affiliated with SoFi, nor do they endorse or sponsor this article. Third-party trademarks referenced herein are property of their respective owners.
Non affiliation: SoFi isn’t affiliated with any of the companies highlighted in this article.
Disclaimer: Many factors affect your credit scores and the interest rates you may receive. SoFi is not a Credit Repair Organization as defined under federal or state law, including the Credit Repair Organizations Act. SoFi does not provide “credit repair” services or advice or assistance regarding “rebuilding” or “improving” your credit record, credit history, or credit rating. For details, see the FTC’s website .
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
External Websites: The information and analysis provided through hyperlinks to third-party websites, while believed to be accurate, cannot be guaranteed by SoFi. Links are provided for informational purposes and should not be viewed as an endorsement.
SOSLR-Q125-022
Read more