Guide to Parent Student Loans
Weighing your child’s college education against keeping your own debt manageable is a tough balancing act. Parent student loans could help you fill gaps when other student aid falls short.
There are a variety of student loans available to parents who are interested in helping their child pay for college. Parents can consider either federal or private student loans. Parent PLUS Loans are federal student loans available to parents. Private lenders will likely have their own loans and terms available for parent borrowers.
Figuring out how to fund your child’s education is a personal decision. Read on for an overview of the different loan types available to parents and some important considerations to make before borrowing money to pay for your child’s education.
Key Points
• Parents can choose between federal Parent PLUS Loans and private student loans to finance education.
• Federal Parent PLUS Loans have a fixed interest rate and cover the full cost of attendance.
• Private loans may offer better rates for good credit but lack federal protections.
• Assess the impact of parent student loans on retirement savings and credit scores before borrowing.
• PLUS Loans offer deferment and consolidation options, while private loans vary by lender.
Types of Parent Student Loans
Parent borrowers can consider borrowing a federal student loan or private student loan. Here are a few of the different types of loans to consider.
Parent PLUS Loans
Parent PLUS Loans are federal student loans that are available to parents of dependent undergraduate students through the Department of Education. They offer fixed interest rates — 8.94% for the 2025-2026 academic year. On the plus side, eligible parents can borrow up to the attendance costs of their child’s school of choice, minus other financial aid.
The amount eligible parents can borrow is not limited otherwise, so this can be a useful loan to fill in whatever tuition gaps aren’t covered by other sources of funding. These loans also provide flexible repayment options, such as graduated and extended repayment plans, as well as deferment and forbearance.
As far as federal loans go, interest rates on Parent PLUS Loans are relatively high. So, it may be worth considering having your child take out other federal loans that carry lower interest rates. Parent PLUS Loans also come with a relatively high origination fee of 4.228% for the 2025-2026 academic year.
Applying for Parent PLUS Loans
To apply for a Parent PLUS Loan, parents will have to fill out the Free Application for Federal Student Aid, or FAFSA®. In addition to the FAFSA, there is a separate application form for Parent PLUS Loans . Most schools accept an online application. For any questions, contact the school’s financial aid office.
Unlike other federal student loans, there is a credit check during the application process for Parent PLUS loans. One of the eligibility requirements is that borrowers not have an adverse credit history. However, parents who do not qualify for a Parent PLUS Loan due to their credit history, may be able to add an endorser in order to qualify. An endorser is someone who signs onto the loan with the borrower and agrees to make payments on the loan if the borrower is unable to do so.
Repaying a Parent PLUS Loan
PLUS Loan terms are limited to 10 to 25 years, depending on the chosen repayment plan, and do not offer income-driven repayment plans like other federal loans do (although they become eligible for the Income-Contingent Repayment Plan if they are consolidated through a Direct Consolidation Loan).
Parents have the option of requesting a deferment if they do not want to make payments on their PLUS loan while their child is actively enrolled in school. If a parent does not request deferment, payments will begin as soon as the loan is disbursed.
Keep in mind that interest will continue to accrue during periods of deferment, so deferring payments while your child is in school may increase the overall cost of borrowing the loan.
Private Parent Student Loans
In some cases, it might make sense to turn to private lenders for student loans. If you have a solid credit history (among other factors), you may be able to secure a reasonable interest rate.
Recommended: Private vs. Federal Student Loans
Before taking on a private student loan, here are some things to be aware of:
• Always read the fine print.
• Origination fees will vary from lender to lender.
• There may not be flexible repayment options, and private loans typically don’t offer deferment or forbearance options the way federal loans do.
• The amount you may qualify to borrow will likely vary.
The application process for private parent student loans will likely differ based on the individual lenders. Repayment terms and options will also generally vary by lender.
Keep in mind that private student loans don’t offer the same borrower protections, like deferment options, as federal student loans. For this reason, they are typically borrowed after other options, like savings, federal student loans, and scholarships, have been exhausted.
💡 Quick Tip: New to private student loans? Visit the Private Student Loans Glossary to get familiar with key terms you will see during the process.
Named a Best Private Student Loans
Company by U.S. News & World Report.
Cosigning Private Student Loan for Your Child
Cosigning a private student loan with your child means that you both have skin in the game. Cosigning a loan typically means each party is equally responsible for the debt. So if your child stops paying, you’re still on the hook for all of the debt.
Most college-age students have had little chance to build their own credit, so having parents — with better, or at least longer, financial histories — as cosigners might mean a better rate than if they applied on their own.
Parents can work out a plan in which both parents and children make payments, or it may even make sense to have a cosigned loan on which only the child makes payments.
Considerations Before Borrowing a Parent Student Loan
As a parent, of course you want the best for your child and to help them in any way you can. Whether or not you decide to take out a student loan to put your child through school is a decision to weigh carefully.
Your choice will likely have a lot to do with your own financial situation. Consider how taking out student loans may affect your own financial goals, especially retirement.
Staying on track for retirement requires a concerted effort during your earning years. That is in part because it can be more difficult to borrow money to cover your retirement expenses when you’re retired, because you will no longer be earning an income to help you pay back borrowed money.
So, before taking on student debt for your children, you’ll probably want to make sure you’re saving enough for your own future. After all, your children likely have decades of potential earnings after they graduate, during which time they can work to pay off their student loans. You, on the other hand, may not have as much time to pay off new debts and save for other goals.
It may also be worth considering how taking on new debt could affect things like your credit score and your debt-to-income ratio. Lenders consider these factors, among others, when deciding whether to loan you money.
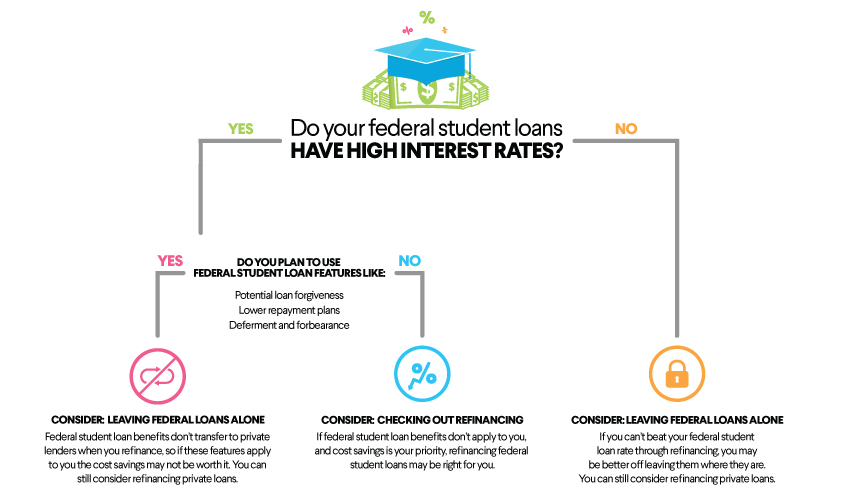
That said, if you feel you are financially strong enough to take on student loans for your child, there are a number of loan options available to you. You may even want to consider refinancing student loans you have if you can qualify for a lower interest rate or more favorable terms.
When you refinance student loans, you replace your existing loans with a new loan from a private lender. If you get a lower interest rate, you may save money on interest over the life of the loan. While it’s possible to refinance both federal and student loans, it’s important to be aware that refinancing federal loans makes them ineligible for federal benefits like income-driven repayment plans and deferment.
The Takeaway
Parent student loans can be borrowed by a student’s parents and used to help pay for educational expenses like tuition. Before borrowing a federal or private parent student loan, parents should evaluate their own financial situation and goals, such as retirement savings.
Looking to lower your monthly student loan payment? Refinancing may be one way to do it — by extending your loan term, getting a lower interest rate than what you currently have, or both. (Please note that refinancing federal loans makes them ineligible for federal forgiveness and protections. Also, lengthening your loan term may mean paying more in interest over the life of the loan.) SoFi student loan refinancing offers flexible terms that fit your budget.
FAQ
Do parents who make $120,000 still qualify for the FAFSA?
There are no income limits to qualify for federal financial aid through the FAFSA. Students, regardless of how much their parents make, should submit the FAFSA. The amount of money the student is eligible to receive will vary based on income, but you may still qualify for certain types of federal aid, including grants and loans.
What are the disadvantages of Parent PLUS loans?
Disadvantages of Parent PLUS loans include the fact that they have relatively high interest rates — 8.94% for the 2025-26 school year (compared to 6.39% for federal Direct loans for undergraduate students). Also, unlike other federal student loans, Parent PLUS loans involve a credit check in order to qualify. Finally, these loans are not eligible for income-driven repayment plans.
What disqualifies you from a Parent PLUS loan?
One thing that could disqualify you for a Parent PLUS loan is if you have an adverse credit history. These loans stipulate that you must not have an adverse credit history in order to be eligible.
However, if your application is denied because of this, you still have options. For example, you could get an endorser who agrees to pay back the loan if you can’t. You can also file an appeal to ask for another review of your application. With either of these options, you will also have to complete PLUS Credit Counseling, which takes about 20 to 30 minutes and can be done online at the Federal Student Aid website.
SoFi Student Loan Refinance
Terms and conditions apply. SOFI RESERVES THE RIGHT TO MODIFY OR DISCONTINUE PRODUCTS AND BENEFITS AT ANY TIME WITHOUT NOTICE. SoFi Private Student loans are subject to program terms and restrictions, such as completion of a loan application and self-certification form, verification of application information, the student's at least half-time enrollment in a degree program at a SoFi-participating school, and, if applicable, a co-signer. In addition, borrowers must be U.S. citizens or other eligible status, be residing in the U.S., Puerto Rico, U.S. Virgin Islands, or American Samoa, and must meet SoFi’s underwriting requirements, including verification of sufficient income to support your ability to repay. Minimum loan amount is $1,000. See SoFi.com/eligibility for more information. Lowest rates reserved for the most creditworthy borrowers. SoFi reserves the right to modify eligibility criteria at any time. This information is subject to change. This information is current as of 4/22/2025 and is subject to change. SoFi Private Student loans are originated by SoFi Bank, N.A. Member FDIC. NMLS #696891 (www.nmlsconsumeraccess.org).
SoFi Loan Products
Terms and conditions apply. SoFi Refinance Student Loans are private loans. When you refinance federal loans with a SoFi loan, YOU FORFEIT YOUR ELIGIBILITY FOR ALL FEDERAL LOAN BENEFITS, including all flexible federal repayment and forgiveness options that are or may become available to federal student loan borrowers including, but not limited to: Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF), Income-Based Repayment, Income-Contingent Repayment, extended repayment plans, PAYE or SAVE. Lowest rates reserved for the most creditworthy borrowers. Learn more at SoFi.com/eligibility. SoFi Refinance Student Loans are originated by SoFi Bank, N.A. Member FDIC. NMLS #696891 (www.nmlsconsumeraccess.org).
SoFi Private Student Loans
Please borrow responsibly. SoFi Private Student loans are not a substitute for federal loans, grants, and work-study programs. We encourage you to evaluate all your federal student aid options before you consider any private loans, including ours. Read our FAQs.
SoFi loans are originated by SoFi Bank, N.A., NMLS #696891 (Member FDIC). For additional product-specific legal and licensing information, see SoFi.com/legal. Equal Housing Lender.
Third-Party Brand Mentions: No brands, products, or companies mentioned are affiliated with SoFi, nor do they endorse or sponsor this article. Third-party trademarks referenced herein are property of their respective owners.
Non affiliation: SoFi isn’t affiliated with any of the companies highlighted in this article.
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
Third Party Trademarks: Certified Financial Planner Board of Standards Center for Financial Planning, Inc. owns and licenses the certification marks CFP®, CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER®
External Websites: The information and analysis provided through hyperlinks to third-party websites, while believed to be accurate, cannot be guaranteed by SoFi. Links are provided for informational purposes and should not be viewed as an endorsement.
SOSLR-Q225-050
Read more