Are You Ready to Buy a House? — Take The Quiz
Buying a house can be the single largest financial move you’ll ever make. What’s more, once purchased, your home is likely to be your biggest asset and possibly a path to building wealth.
So this rite of passage probably isn’t something to be done without a lot of preparation. For instance, when preparing to buy a home, you usually have to focus on such factors as:
• Saving for a down payment
• Optimizing your credit score
• Understanding what your monthly expenses will be
• Considering the dynamics of the real-estate market
• Researching where you want to live
• Making sure you’re ready for the responsibilities of homeownership.
You’ll learn more about these factors in a minute, but first, take this quiz to get a read on just how ready you are to dive into house-buying. While it won’t answer the question, “Am I ready to buy a house?” definitively, it can help you gauge where you stand.
Then, read on to learn more about how to make snagging your dream house become a reality.
Key Points
• Financial readiness involves saving for a down payment, optimizing credit scores, and understanding monthly expenses.
• Real estate market dynamics and preapproval provide a competitive edge in homebuying.
• Home maintenance requires budgeting and time for repairs and regular upkeep.
• Community integration involves settling in one area for several years to recoup costs.
• A favorable debt-to-income ratio and credit score improve mortgage offers and interest rates.
Home Buyer Readiness Quiz
Now that you’ve taken the quiz, here’s more intel on how to get ready to buy a house.
Recommended: First-Time Home Buyer Guide
Financial Factors
Home ownership can be quite expensive, and has become especially pricey in recent years. As you may know, housing prices soared during the pandemic, rising over 40% in some areas. In an effort to stem that, as well as other aspects of inflation, the Fed has been raising interest rates, so it’s become more expensive to borrow money, too, further squeezing potential homebuyers.
But don’t let that discourage you: Homeownership is still a goal you can realize, especially if you prepare for the following:
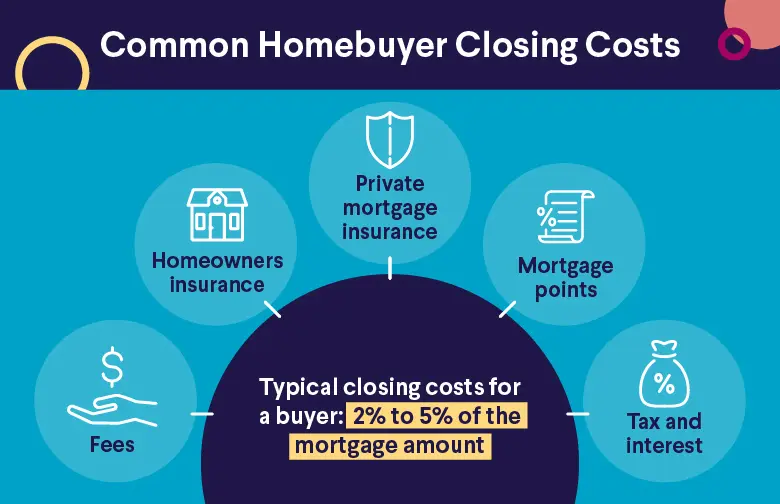
• Down payment: Ideally, lenders like to see a 20% down payment (although SoFi offers flexible down payment options). Plus, you’ll need to have enough money left over for closing costs, moving costs, and any renovation costs involved.
• Private mortgage insurance: If you are putting down less than 20% on your home purchase, you may have to pay private mortgage insurance (PMI). This helps protect your lender as you may look like a less well-qualified home purchaser. This cost is typically charged along with your monthly interest payment by the lender. It’s wise to include this amount in your calculations, if necessary, as you move toward buying a house.
• Income: Knowing the answer to “When can I buy a house?” doesn’t depend on a particular salary. However, mortgage lenders do like to see two years of steady income, because both job continuity and consistent income are important.
• Debt-to-income (DTI) ratio: You’ll need to see if your monthly income allows you to afford the mortgage payment you’d be taking on. This typically involves calculating your debt-to-income ratio or DTI.
Here’s an example: Say you make $6,000 a month, before taxes. You’re paying $1,500 a month in rent, and when you add in car payments, credit card debt, and student loan payments, that equals another $700. You’ve got monthly expenses, then, of $2,200; when you divide that by your monthly income ($2,200/$6,000), then your debt-to-income ratio is 36.7%, which is in the range of what many lenders like to see.
• Credit score: It’s helpful to know your credit score before you go home shopping and, if it’s under 700 (meaning either at the low end of a good score or a fair credit score), work to build it. That can open you up to more mortgage offers and lower interest rates.
• Mortgage options: Speaking of mortgages, connecting with lenders or mortgage brokers can help you gain a better understanding of how much house you can afford, what kinds of mortgages are available, and whether you can get prequalified or even preapproved before you shop in earnest. This can give you an edge in or possibly even be necessary in today’s tight housing market.
• Homeownership costs: In addition to the mortgage payment and any PMI, you’ll need to budget for property taxes, heating costs, and other regular expenses. Make sure to factor those in as you develop a budget for your life as a homeowner.
Get matched with a local
real estate agent and earn up to
$9,500‡ cash back when you close.
Pair up with a local real estate agent through HomeStory and unlock up to
$9,500 cash back at closing.‡ Average cash back received is $1,700.
Recommended: How to Qualify for a Mortgage
Housing Market Conditions
When determining if you’re ready to buy a house, also consider housing market conditions. Among the key factors:
• Location: Of course, you’ll want your home to be in a desirable location, however you define “desirable.” It could mean being in the heart of a busy city — or in a peaceful place along a river. If you have or plan to have a family, quality schools are likely important, and so forth.
It’s likely going to make your house hunt more manageable and productive if you narrow down where you want to live to a few towns or neighborhoods. Otherwise, you might spend a lot of time and effort driving all over and not being able to whittle down the choices.
• Real-estate dynamics: In desirable locations, competition is fierce today, with homes often selling quickly after being put up for sale and bidding wars occurring. And, as demand has increased, available housing (especially for first-time homebuyers looking to purchase in affordable price ranges) has therefore decreased.
So, you’ll have to be prepared to compete in the current housing market conditions, which means having your financial situation in order so you can make a timely offer on a house of choice.
Check out local real estate
market trends to help with
your home-buying journey.
Lifestyle Considerations
Let’s say you’re confident that you have the financial resources to purchase a home in your neighborhood of choice. Before you move forward, here are a couple of lifestyle issues to consider:
• Home maintenance: If you’re used to renting, your landlord has played a key role in home repairs and so forth. If you buy a home, you would now be your own landlord. That means dealing with broken boilers, leaky roofs, yard maintenance, and more. Be sure you budget for that financially and are also prepared for the responsibility.
• Community: Think about whether you are ready to settle down in a particular community for at least a few years. If not, you may not break even when you sell the house you bought. Here’s why: It can take time to recoup closing costs and other expenses you covered when purchasing the home.
The Takeaway
Homeownership can be the foundation of the American dream for many people. It’s also a potential avenue to build wealth. But when you should buy a house depends on a variety of factors. Before you dive in, do your research, save for your down payment, and optimize your finances so you are ready to handle the responsibility.
Looking for an affordable option for a home mortgage loan? SoFi can help: We offer low down payments (as little as 3% - 5%*) with our competitive and flexible home mortgage loans. Plus, applying is extra convenient: It's online, with access to one-on-one help.
[kicker_hl_lock_days]
SoFi Mortgages
Terms, conditions, and state restrictions apply. Not all products are available in all states. See SoFi.com/eligibility-criteria for more information.
SoFi Loan Products
SoFi loans are originated by SoFi Bank, N.A., NMLS #696891 (Member FDIC). For additional product-specific legal and licensing information, see SoFi.com/legal. Equal Housing Lender.
*SoFi requires Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI) for conforming home loans with a loan-to-value (LTV) ratio greater than 80%. As little as 3% down payments are for qualifying first-time homebuyers only. 5% minimum applies to other borrowers. Other loan types may require different fees or insurance (e.g., VA funding fee, FHA Mortgage Insurance Premiums, etc.). Loan requirements may vary depending on your down payment amount, and minimum down payment varies by loan type.
Qualifying for the reward requires using a real estate agent that participates in HomeStory’s broker to broker agreement to complete the real estate buy and/or sell transaction. You retain the right to negotiate buyer and or seller representation agreements. Upon successful close of the transaction, the Real Estate Agent pays a fee to HomeStory Real Estate Services. All Agents have been independently vetted by HomeStory to meet performance expectations required to participate in the program. If you are currently working with a REALTOR®, please disregard this notice. It is not our intention to solicit the offerings of other REALTORS®. A reward is not available where prohibited by state law, including Alaska, Iowa, Louisiana and Missouri. A reduced agent commission may be available for sellers in lieu of the reward in Mississippi, New Jersey, Oklahoma, and Oregon and should be discussed with the agent upon enrollment. No reward will be available for buyers in Mississippi, Oklahoma, and Oregon. A commission credit may be available for buyers in lieu of the reward in New Jersey and must be discussed with the agent upon enrollment and included in a Buyer Agency Agreement with Rebate Provision. Rewards in Kansas and Tennessee are required to be delivered by gift card.
HomeStory will issue the reward using the payment option you select and will be sent to the client enrolled in the program within 45 days of HomeStory Real Estate Services receipt of settlement statements and any other documentation reasonably required to calculate the applicable reward amount. Real estate agent fees and commissions still apply. Short sale transactions do not qualify for the reward. Depending on state regulations highlighted above, reward amount is based on sale price of the home purchased and/or sold and cannot exceed $9,500 per buy or sell transaction. Employer-sponsored relocations may preclude participation in the reward program offering. SoFi is not responsible for the reward.
SoFi Bank, N.A. (NMLS #696891) does not perform any activity that is or could be construed as unlicensed real estate activity, and SoFi is not licensed as a real estate broker. Agents of SoFi are not authorized to perform real estate activity.
If your property is currently listed with a REALTOR®, please disregard this notice. It is not our intention to solicit the offerings of other REALTORS®.
Reward is valid for 18 months from date of enrollment. After 18 months, you must re-enroll to be eligible for a reward.
SoFi loans subject to credit approval. Offer subject to change or cancellation without notice.
The trademarks, logos and names of other companies, products and services are the property of their respective owners.
Third-Party Brand Mentions: No brands, products, or companies mentioned are affiliated with SoFi, nor do they endorse or sponsor this article. Third-party trademarks referenced herein are property of their respective owners.
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
SOHL-Q225-015
Read more