What the Binomial Option Pricing Model Is & How It Works
Editor's Note: Options are not suitable for all investors. Options involve risks, including substantial risk of loss and the possibility an investor may lose the entire amount invested in a short period of time. Please see the Characteristics and Risks of Standardized Options.
The binomial option pricing model is a valuation tool that predicts the price of an asset for selected future points in time then uses an iterative approach to work backwards to determine the present value of options on that underlying asset.
The binomial option pricing model has the benefit of being relatively easy to implement and provides visibility into the linkages between the underlying asset price and the option prices as the expiration date approaches.
What Is the Binomial Option Pricing Model?
The binomial option pricing model is a widely used option pricing formula. There are multiple versions of the model, depending on what assumptions the trader wishes to make and what types of options are to be priced.
Fundamentally, the model involves a three-step process:
1. Generate the binomial price tree for the underlying asset.
2. Calculate the options values based on the asset prices for each final node.
3. Calculate the option value at each preceding node.
Recommended: How to Trade Options
Assumptions of the Binomial Option Pricing Model
The binomial option pricing model assumes two possible outcomes: an up or down change in the stock price. While it’s simple in a one-period approach, the model can quickly turn complex over multiple time frames. However, constructing the pricing tree illustrates how an asset’s price changes from period to period.
Another advantage is that the binomial option pricing model can be used to value American, European, and Bermuda-style options. There are adjustments needed to use the binomial model based on which options are being priced. For this discussion, we will focus on American options only.
Other assumptions in the model discussed herein include that the underlying asset pays no dividends, the interest rate is constant, there are no transaction costs, there are no taxes, and that the risk-free rate is constant.
It also assumes investors are risk-neutral.
💡 Quick Tip: If you’re an experienced investor and bullish about a stock, buying call options (rather than the stock itself) can allow you to take the same position, with less cash outlay. It is possible to lose money trading options, if the price moves against you.
How Does the Binomial Model Work?
The binomial option tree is used for finding the current value of an option. This value is equal to the present value of the probability-weighted future payoffs.
Binomial Option Pricing Model Calculations
Let’s dive into calculations for calls and puts. In order to understand how these calculations are made it helps to know the basics of options trading strategies.
Call Options
A call option gives the holder the right but not the obligation to purchase a security at a specific price at a specific time. A call option is in the money when the stock price is above the strike price. A binomial tree’s nodes will value an option at the maximum of zero or its calculated value.
Recommended: How Options Are Priced
When the underlying asset moves up in price, the call option’s payoff (Cup) is the maximum of zero and the stock price (S) multiplied by the up factor (u) and reduced by the exercise price (Px).
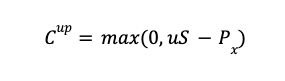
When the underlying asset moves down in price, the call option’s payoff (Cdown) is the maximum of zero and the stock price (S) multiplied by the down factor (d) and reduced by the exercise price (Px).
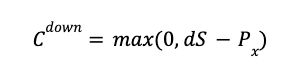
The binomial model calculates all possible payoffs, based on these calculations. The final outcomes are then discounted back to calculate the present value.
Put Options
Put options give the holder the right but not the obligation to sell a security at a specific price at a specific time. A put option is in the money when the stock price is below the strike price.
When the underlying asset moves up in price, the put option’s payoff (Pup) is the maximum between zero and the exercise price (Px) minus the stock price (S) multiplied by the up factor (u).
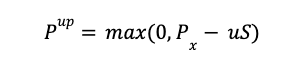
When the underlying asset moves down in price, the put option’s payoff (Pdown) is the maximum between zero and the exercise price (Px) minus the stock price (S) multiplied by the down factor (d).
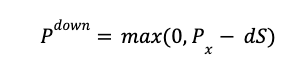
Binomial Model Example
Assumptions
XYZ stock is currently trading at $100 and you wish to calculate the value of a call option with a $105 strike price that will expire in two weeks.
You expect that each week the stock may increase by 10% or decrease by 15%. The risk-free rate is currently 5% and you will be looking for cash settlement rather than delivery of shares. Additionally, XYZ is not expected to pay dividends over the two-week holding period.
You want to view how the option price will move weekly up until expiration and calculate the option value today.
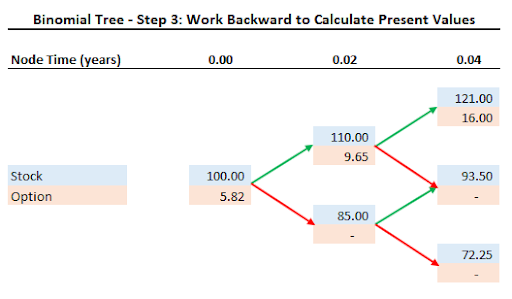
Generate the Binomial Tree
We construct the binomial tree for the prices of XYZ stock.
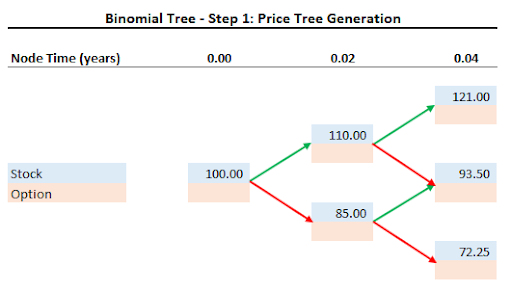
At the end of one week (1/52 of a year or 0.02 years) the stock will be priced at either $110 or $85.
After two weeks, (0.04 years) the price will increase to $121 if the price moves up twice in a row. The stock price will be $93.50 if the price moves up then down, or down then up. Finally, if the stock moves down twice in a row the stock will drop to $72.25.
Note that we can create a binomial tree for any time period size and include many more steps at the cost of greater complexity in the calculations.
Calculate Final Option Values
Having forecast the stock price two weeks into the future we can calculate the value of the $105 strike price call option at that time.
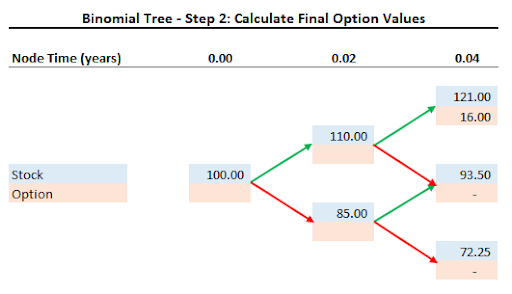
The call option will only have value if the stock moves up twice in a row. At that time the shares will be worth $121 and the option will be worth $16.
Work Backward to Calculate Present Values
Before we can perform the present value calculations we need to determine the probability that the stock price, and the call option price, will move along the upward path in the binomial tree during each week.
Fortunately we have all the information we need to calculate the probability based on our initial assumptions. The probability for an up move is:
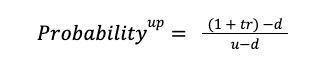
Where:
• t = the time period in years (1 week = 0.02 years)
• r = the risk-free rate (5%)
• u = up factor ($110 / $100 = 1.1)
• D = down factor ($85 / $100 = 0.85)
Substituting into the equation:
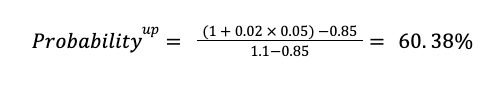
Because there are only two paths at each node the the probability of a down move is:

Given the probabilities and the potential option values at the end of week two, we use the present value calculation to determine the option value for the end of week one.
We repeat this process until we arrive at the value of the call option today.
At each step we weigh the final values by their respective probabilities and discount by the risk-free rate using the following equation:
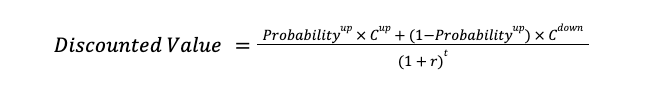
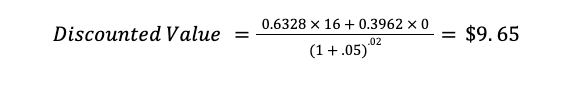
Finally, we arrive at the present value of the call option of $5.82.
Finally, user-friendly options trading is here.*
Trade options with SoFi Invest on an easy-to-use, intuitively designed online platform.
*Check out the OCC Options Disclosure Document.
Pros and Cons of the Binomial Model
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Simple to calculate | Difficult to predict future prices and probabilities |
| Can be used on American options | Assumes conditions that are not seen in real-world markets |
| Can be used over multiple periods | Complexity grows as more periods are considered |
Binomial Option Pricing Model vs Black-Scholes Model
The Black-Scholes model comes to a deterministic result based on the inputs. Its inputs are option variables such as the strike price, the current stock price, the time to expiration, the risk-free rate, and the volatility. While the binomial model is considered path dependent, the Black-Scholes model is path independent.
Widely used in practice and considered accurate, the Black-Scholes model makes assumptions that sometimes arrive at options prices that are different from those seen in the real world.
The Black-Scholes model is considered the standard when valuing European options since the model does not allow for options to be exercised early.
| Binomial Option Pricing Model | Black-Scholes Model |
|---|---|
| Probabilistic approach | Deterministic approach |
| Path dependent with two possible outcomes at each node | Usually accurate, but output prices sometimes deviate from those seen in the real world |
| Helpful for American options | Helpful for European options |
Binomial Option Pricing Model vs Monte Carlo Model
The Monte Carlo model runs thousands of computer simulations to arrive at a solution. Monte Carlo simulation often includes an array of possible paths — some that show higher ending prices and others that show lower prices.
The computer simulations are only as good as the assumptions used. Analysts can tailor the inputs. Often, historical data is used in Monte Carlo simulations which may lead to results that aren’t applicable.
| Binomial Option Pricing Model | Monte Carlo Model |
|---|---|
| An iterative approach that is path dependent | Based on computer simulations |
| Less computer intensive | You can tailor the inputs and scenarios |
| Uses future assumptions, not historical data | Output only as good as the assumptions used |
The Takeaway
The binomial option pricing model is a valuation tool that predicts the price of an asset for selected future points in time then uses an iterative approach to work backwards to determine the present value of options on that underlying asset.
Due to its relative simplicity and speed, traders often prefer it to the Black-Scholes and Monte Carlo models.
SoFi’s options trading platform offers qualified investors the flexibility to pursue income generation, manage risk, and use advanced trading strategies. Investors may buy put and call options or sell covered calls and cash-secured puts to speculate on the price movements of stocks, all through a simple, intuitive interface.
With SoFi Invest® online options trading, there are no contract fees and no commissions. Plus, SoFi offers educational support — including in-app coaching resources, real-time pricing, and other tools to help you make informed decisions, based on your tolerance for risk.
FAQ
Who developed the binomial model?
The binomial options pricing model was first suggested by William Sharpe in 1978, but the model’s development is associated with work done by John Cox, Stephen Ross, and Mark Rubinstein in 1979.
Are the Black-Scholes and binomial option pricing models the same?
No, these are two different models. The Black-Scholes model provides a numerical result based on inputs. The binomial options pricing model prices an asset based on a range of possible results. The binomial model is considered an iterative calculation since there is a range of possible outcomes to value options. The Black Scholes model uses fixed inputs to arrive at an option’s value.
How is the binomial option pricing model different from the Monte Carlo model?
The Monte Carlo model runs thousands of computer simulations to eventually arrive at an options price. The model first generates a random number based on a probability distribution. That number then uses additional option inputs like volatility and time to expiration to generate a stock price. The stock price at expiration is then used to calculate the value of the option. The result is only as good as the inputs used.
The model runs that process thousands of times, using different variables from the probability functions. To determine option pricing, the Monte Carlo model uses the average of all the calculated results.
Photo credit: iStock/David Petrus Ibars
INVESTMENTS ARE NOT FDIC INSURED • ARE NOT BANK GUARANTEED • MAY LOSE VALUE
For disclosures on SoFi Invest platforms visit SoFi.com/legal. For a full listing of the fees associated with Sofi Invest please view our fee schedule.
Options involve risks, including substantial risk of loss and the possibility an investor may lose the entire amount invested in a short period of time. Before an investor begins trading options they should familiarize themselves with the Characteristics and Risks of Standardized Options . Tax considerations with options transactions are unique, investors should consult with their tax advisor to understand the impact to their taxes.
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
SOIN1221525




