The Strategic Guide to Early Retirement
An early retirement used to be considered a bit of a dream, but for many people it’s a reality — especially those who are willing to budget, save, and invest with this goal in mind.
If you’d like to retire early, there are concrete steps you can take to help reach your goal. Here’s what you need to know about how to retire early.
Key Points
• Early retirement requires significant savings, often guided by the Rule of 25, which suggests saving 25 times annual expenses.
• The FIRE movement encourages saving 50-75% of income to retire early.
• Effective budgeting and reducing expenses are crucial for accumulating necessary retirement funds.
• Investment strategies should balance growth and risk, adjusting as retirement nears.
• Health insurance planning is essential when retiring before qualifying for Medicare at age 65.
Understanding Early Retirement
Early retirement typically refers to retiring before the age of 65, which is when eligibility for Medicare benefits begins. Some people may want to retire just a few years earlier, at age 60, for instance. But others dream of retiring in their 40s or 50s or even younger.
Clarifying Early Retirement Age and Goals
You’re probably wondering, how can I retire early? That’s an important question to ask. First, though, you have to decide at what age to retire.
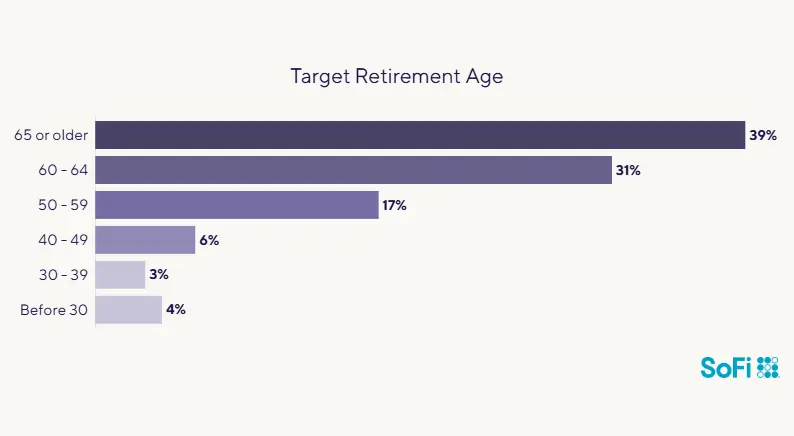
Some people dream of retiring at 50 — or even earlier. According to SoFi’s 2024 Retirement Survey of 500 U.S. adults, 12% want to retire at age 49 or younger. Here’s how that group respondents breaks down:
Source: SoFi Retirement Survey, April 2024
Reasons for Retiring
In the same 2024 SoFi retirement survey, respondents cite the following as the top factors influencing their reasons to retire:
Insights into the Financial Independence, Retire Early (FIRE) Movement
There’s a movement of people who want to retire early. It’s called the FIRE movement, which stands for “financially independent, retire early.” FIRE has become a worldwide trend that’s inspiring people to work toward retiring in their 50s, 40s, and even their 30s. In the 2024 SoFi Retirement Survey, 12% of respondents say the retirement age they’re aiming for is 49 or younger.
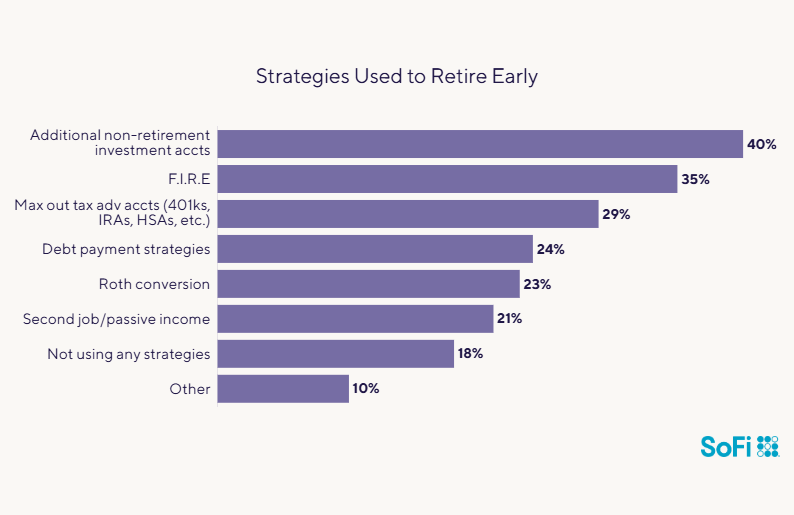
Here’s how FIRE works: In order to retire at a young age, people who follow the movement allocate 50% to 75% of their income to savings. However, that can be challenging because it means they have to sacrifice certain lifestyle pleasures such as eating out or traveling. Of the SoFi survey respondents who said they want to retire at age 49, 18% are not using any strategies that might help them retire early.
Another 35% of that group are using the FIRE method, while others are using a variety of different methods to try to reach their early retirement goal as shown here:

Source: SoFi Retirement Survey, April 2024
💡 Quick Tip: Did you know that a traditional IRA, is a tax-deferred account? That means you don’t pay taxes on the money you put in it (up to an annual limit) or the gains you earn, until you retire and start making withdrawals.
Financial Planning for Early Retirement
In order to start planning to retire early, first ask yourself how confident you are about pulling it off. In the SoFi Retirement Survey, 68% of respondents say they are very or somewhat confident in their ability to retire at their target age, while 15% are very or somewhat doubtful they can do it.
Once you’ve assessed your confidence level, the next step is to calculate how much money you’ll need to live on once you stop working. How much would you have to save and invest to arrive at an amount that would allow you to retire early? Here’s how to help figure that out.
Many people wonder: How much do I need to retire early? There isn’t one answer to that question. The right answer for you is one that you must arrive at based on your unique needs and circumstances. That said, to learn whether you’re on track for retirement it helps to begin somewhere, and the Rule of 25 may provide a good ballpark estimate.
The Rule of 25 recommends saving 25 times your annual expenses in order to retire. Why? Because according to one rule of thumb, you should only spend 4% of your total nest egg every year. By limiting your spending to a small percentage of your savings, the logic goes, your money is more likely to last.
Here’s an example: if you spend $75,000 a year, you’ll need a nest egg of $1,875,000 in order to retire.
$75,000 x 25 = $1,875,000
With that amount saved, and assuming an annual withdrawal rate of 4%, you would have $75,000 per year in income.
Obviously, this is just an example. You might need less income in retirement or more — perhaps a lot less or a lot more, depending on your situation. If your desired income is $50,000, for example, you’d need to save $1,250,000.
The Benefits of Social Security
Once you reach the age of 62, which some consider a traditional retirement age, you are then able to claim Social Security benefits. (Age 67 is considered “full retirement” age for those born in 1960 and later, and you can wait to claim benefits until age 70.)
The longer you wait to claim Social Security, the higher your monthly payments will be. You could add those Social Security benefits to your income or consider reinvesting the money, depending on your circumstances as you get older.
Recommended: Typical Retirement Expenses to Prepare For
Effective Savings Strategies
How do you save the amount of money you’d need for your early retirement plan?
Having a budget you can live with is critical to making this plan a success. The essential word here isn’t budget, it’s the whole phrase: a budget you can live with.
There are countless ways to manage how you budget. There’s the 50-30-20 plan, the envelope method, the zero-based budget, and so on. You could test a couple of them for a couple of months each in order to find one you can live with.
Another strategy for saving more is to get a side hustle to bring in some extra income. You can put that money toward your early retirement goal.
Adjusting Your Financial Habits
As you consider how to retire early, one of the first things you’ll need to do is cut your expenses now so that you can save more money. These strategies can help you get started.
Lifestyle Changes to Accelerate Savings
Take a look at your current spending and expenses and determine where you could cut back. Maybe instead of a $4,000 vacation, you plan a $2,000 trip instead, and then save or invest the other $2,000 for retirement.
You may be able to live more of a minimalist lifestyle overall. Rather than buying new clothes, for instance, search through your closets for items you can wear. Eat out less and cook at home more. Cut back on some of the streaming services you use. Scrutinize all areas of your spending to see what you can eliminate or pare back.
Debt Management Before Retirement
Obviously, it’s very difficult to achieve a big goal like saving for an early retirement if you’re also trying to pay down debt. It’s wise to work to pay off any and all debts you might have (credit card, student loan, personal loan, car loan, etc.).
That’s not only because being debt-free feels better — it also saves you money. For example, the interest rate you’re paying on credit card or store cards can be quite high, often above 15% or even 20%. If you owe $6,000 on a credit card at 17% interest, for example, when you pay that off, you’re essentially saving the interest that debt was costing you each year.
Health Care Planning: A Critical Component of Early Retirement
When you retire early, you need to think about health insurance since you’ll no longer be getting it through your employer. Medicare doesn’t begin until age 65, so start researching the private insurance market now to understand the different plans available and what you might need.
It’s critical to have the right health insurance in place, so make sure you devote proper time and attention to this task.
Investment Management for Future Retirees
Next up, you’ll need to decide what to invest in and how much to invest in order to grow your savings without putting it at risk.
Understanding Your Investment Options
How do you invest to retire early? You can invest in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), target date funds, and more.
One major factor to consider is how aggressively you want to invest. That means: Are you ready to invest more in equities, say, taking on the potential for greater risk in order to possibly reap potential gains? Or would you feel more at ease if you invested using a more conservative strategy, with less exposure to risk (but potentially less reward)?
Whichever strategy you choose, you may want to invest on a regular cadence. This approach, called dollar-cost averaging, is one way to maximize potential market returns and mitigate the risk of loss.
Balancing Growth and Risk in Your Investment Portfolio
Because you have less time to save for retirement, you will likely want your investments to grow. But you also need to consider your risk tolerance, as mentioned above. Think about a balanced, diversified portfolio that has the potential to give you long-term growth without taking on more risk than you are comfortable with.
As you get closer to your early retirement date, you can move some of your savings into safer, more liquid assets so that you have enough money on hand for your living, housing, and healthcare expenses.
Retirement Accounts: 401(k)s, IRAs, and HSAs
If your employer offers a retirement plan like a 401(k) or 403(b), that’s the first thing you want to take advantage of — especially if your employer matches a percentage of your savings.
The other reason to save and invest in an employer-sponsored plan is that in most cases the money you save the plan reduces your taxable income. These accounts are considered tax deferred because the amount you save is deducted from your gross income. So the more you save, the less you might pay in taxes. You do pay ordinary income tax on the withdrawals in retirement, however.
The caveat here is that you can’t access those funds before you’re 59½ without paying a penalty. So if you plan to retire early at 50, you will need to tap other savings for roughly the first decade to avoid the withdrawal penalties you’d incur if you tapped your 401(k) or Individual Retirement Account (IRA) early.
Be sure to find out from HR if there are any other employee benefits you might qualify for, such as stock options or a pension, for instance.
Additionally, if your employer offers a Health Savings Account as part of your employee benefits, you might consider opening one.
A Health Savings Account allows you to save additional money: For tax year 2025, the HSA contribution caps are $4,300 for individuals and $8,550 for family coverage. For tax year 2026, the HSA contribution caps are $4,400 for individuals and $8,750 for family coverage.
Your contributions are considered pre-tax, similar to 401(k) or IRA contributions, and the money you withdraw for qualified medical expenses is tax free (although you’ll pay taxes on money spent on non-medical expenses).
Finally, consider opening a Roth IRA. The advantage of saving in a Roth IRA vs. a regular IRA is that you’re contributing after-tax money that can be withdrawn penalty- and tax-free at any time.
To withdraw your earnings without paying taxes or a penalty, though, you must have had the account for at least five years (as per the Roth IRA 5-Year Rule), and you must be over 59 ½.
Recommended: How to Open an IRA in 5 Steps
The Pillars of Early Retirement
Retiring early means you’ll need to have income coming in to help support you. You may have a pension, which can also help. Once you’ve identified the income you’ll be generating, you’ll need to withdraw it in a manner that will help it last over the years of your retirement.
Establishing Multiple Income Streams
Having different streams of income is important so that you’re not just relying on one type of money coming in. For instance, your investments can be a source of potential income and growth, as mentioned. In addition, you may want to get a second job now in addition to your full-time job — perhaps a side hustle on evenings and weekends — to generate more money that you can put toward your retirement savings.
The Role of Social Security and Pensions in Early Retirement
Social Security can help supplement your retirement income. However, as covered above, the earliest you can collect it is at age 62. And if you take your benefits that early they will be reduced by as much as 30%. On the other hand, if you wait until full retirement age to collect them, you’ll receive full benefits. If you were born in 1960 or later, your full retirement age is 67. You can find out more information at ssa.gov.
If your employer offers a pension, you should be able to collect that as another income stream for your retirement years. Generally, you need to be fully vested in the plan to collect the entire pension. The amount you are eligible for is typically based on what you earned, how long you worked for the company, and when you stop working there. Check with your HR department to learn more.
The Significance of Withdrawal Strategies: Rules of 55 and 4%
When it comes to withdrawing money from your investments after retirement, there are some rules and guidelines to be aware of. According to the Rule of 55, the IRS allows certain workers who leave their jobs to take penalty-free distributions from their current employer’s workplace retirement account, such as a 401(k) or 403(b), the year they turn 55.
The 4% rule is a general rule of thumb that recommends that you take 4% of your total retirement savings per year to cover your expenses.
To figure out what you would need, start with your desired yearly retirement income, subtract the annual amount of any pension or additional revenue stream you might have, and divide that number by 0.4. The resulting amount will be 4%, and you can aim to withdraw no more than that amount every year. The rest of your money would stay in your retirement portfolio.
Monitoring Your Progress Towards Early Retirement
To stay on course to reach your goal of early retirement, keep tabs on your progress at regular intervals. For instance, you may want to do a monthly or bi-monthly financial check-in to see where you’re at. Are you saving as much as you planned? If not, what could you do to save more?
Using an online retirement calculator can help you keep track of your goals. From there you can make any adjustments as needed to help make your dreams of early retirement come true.
How to Manage Early Retirement When You Get There
The budget you make in order to save for an early retirement is probably a good blueprint for how you should think about your spending habits after you retire. Unless your expenses will drop significantly after you retire (for instance, if you move or need one car instead of two, etc.), you can expect your spending to be about the same.
That said, you may be spending on different things. Whatever your retirement looks like, though, it’s wise to keep your spending as steady as you can, to keep your nest egg intact.
The Takeaway
An early retirement may appeal to many people, but it takes a real commitment to actually embrace it as your goal. These days, many people are using movements like FIRE (financial independence, retire early) to help them take the steps necessary to retire in their 30s, 40s, and 50s.
You can also make progress toward an early retirement by determining how much money you’ll need for post-work life, budgeting, and cutting back on expenses . And by saving and investing wisely, you may be able to make your goal a reality.
Prepare for your retirement with an individual retirement account (IRA). It’s easy to get started when you open a traditional or Roth IRA with SoFi. Whether you prefer a hands-on self-directed IRA through SoFi Securities or an automated robo IRA with SoFi Wealth, you can build a portfolio to help support your long-term goals while gaining access to tax-advantaged savings strategies.
FAQs
How much do you need to save for early retirement?
There isn’t one right answer to the question of how much you need to save for early retirement. It depends on your specific needs and circumstances. However, as a starting point, the Rule of 25 may give you an estimate. This guideline recommends saving 25 times your annual expenses in order to retire, and then following the 4% rule, and withdrawing no more than 4% a year in retirement to cover your expenses.
Is early retirement a practical goal?
For some people, early retirement can be a practical goal if they plan properly. You’ll need to decide at what age you want to retire, and how much money you’ll need for your retirement years. Then, you will need to map out a budget and a concrete strategy to save enough. It will likely require adjusting your lifestyle now to cut back on spending and expenses to help save for the future, which can be challenging.
INVESTMENTS ARE NOT FDIC INSURED • ARE NOT BANK GUARANTEED • MAY LOSE VALUE
For disclosures on SoFi Invest platforms visit SoFi.com/legal. For a full listing of the fees associated with Sofi Invest please view our fee schedule.
Tax Information: This article provides general background information only and is not intended to serve as legal or tax advice or as a substitute for legal counsel. You should consult your own attorney and/or tax advisor if you have a question requiring legal or tax advice.
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs): Investors should carefully consider the information contained in the prospectus, which contains the Fund’s investment objectives, risks, charges, expenses, and other relevant information. You may obtain a prospectus from the Fund company’s website or by emailing customer service at [email protected]. Please read the prospectus carefully prior to investing.
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
SOIN0224019
CN-Q425-3236452-112