Guide to Yield to Maturity (YTM)
When investors evaluate which bonds to buy, they often take a look at yield to maturity (YTM), the total rate of return a bond will earn over its life, assuming it has made all interest payments and repaid the principal.
Calculating YTM can be complicated. Doing so takes into account a bond’s face value, current price, number of years to maturity and coupon, or interest payments. It also assumes that all interest payments are reinvested at a constant rate of return. With these figures in hand, they will be better equipped to understand the bond market and which bonds will offer the greatest yield if held to maturity.
Key Points
• Yield to Maturity (YTM) represents the total return expected from holding a bond until it matures, factoring in interest payments and principal repayment.
• Calculating YTM involves the bond’s coupon rate, face value, current market price, and the time to maturity, making it a complex formula.
• YTM is useful for comparing bonds with different characteristics, helping investors anticipate returns and understand interest rate risks associated with bond investments.
• Limitations of YTM include assumptions about reinvestment of interest payments and the neglect of taxes, which can significantly affect actual returns.
• Investors can utilize YTM as a tool for decision-making but should consider diversifying their portfolios and possibly consulting financial professionals for guidance.
What Is Yield to Maturity (YTM)?
The yield to maturity (YTM) is the estimated rate investors earn when holding a bond until it reaches maturity or full value. The YTM is stated as an annual rate and can differ from the stated coupon rate.
The calculations in the yield to maturity formula include the following factors:
• Coupon rate: Also known as a bond’s interest rate, the coupon rate is the regular payment issuers pay bondholders for the right to borrow their money. The higher the coupon rate, the higher the yield.
• Face value: A bond’s face value, or par value, is the amount paid to a bondholder at its maturity date.
• Market price: A bond’s market price refers to how much an investor would have to pay for a bond on the open market currently. The price buyers pay on the secondary market may be higher or lower than a bond’s face value. The higher the price of the bond, the lower the yield.
• Maturity date: The date when the issuer repays the principal is known as the maturity date.
The YTM formula assumes all coupon payments are made as scheduled, and most calculations assume interest will be reinvested.
Get up to $1,000 in stock when you fund a new Active Invest account.*
Access stock trading, options, alternative investments, IRAs, and more. Get started in just a few minutes.
How to Calculate Yield to Maturity
Calculating yield to maturity can be done by following a formula — but fair warning, it’s not simple arithmetic!
Yield to Maturity (YTM) Formula
To calculate yield to maturity, investors can use the following YTM formula:
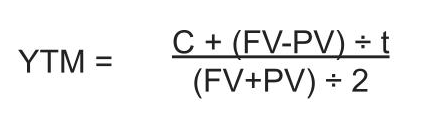
In this calculation:
C = Interest or coupon payment
FV = Face value of the investment
PV = Present value or current price of the investment
t = Years it takes the investment to reach the full value or maturity
Example of YTM Calculation
Here’s an example of how to use the YTM formula.
Suppose there’s a bond with a market price of $800, a face value of $1,000, and a coupon value of $150. The bond will reach maturity in 10 years, with a coupon rate of about 14%.
By using this formula, the estimated yield to maturity would calculate as follows:
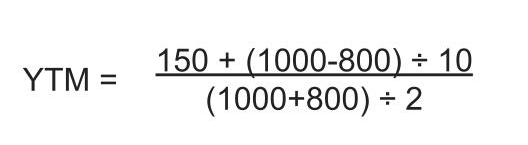
The Importance of Yield to Maturity
Knowing a bond’s YTM can help investors compare bonds with various maturity and coupon rates, and ultimately, what their dividend yield could look like. For example, consider two bonds of varying maturity: a five-year bond with a 3% YTM and a 10-year bond with a 2.5% YTM. Investor’s can easily see that the five-year bond is more valuable.
YTM is particularly useful when attempting to compare older bonds sold in a secondary market, which can be priced at a premium or discounted — meaning they cost more or less than the bond’s face value. Understanding the YTM formula also helps investors understand how market conditions can impact their portfolio based on the investment they select. Since yields rise when prices drop (and vice versa) as seen on a yield curve, investors can forecast how their investment will perform.
Additionally, YTM can help investors understand how likely they are to be affected by interest rate risk — the danger that the value of a bond may be adversely affected due to the changes in interest rate. Current YTM is inversely proportional to interest rate risk. That means, the higher the YTM, the less bond prices will be affected should interest rates change, in theory.
Yield to Maturity vs Yield to Call
With a callable, or redeemable bond, issuers can choose to repay the principal amount before the maturity date, halting interest payments early. This throws a bit of a wrench into the YTM calculation. Instead, investors may want to use a yield to call (YTC) calculation. To do so, they can use the YTM calculation, substituting the maturity date for the soonest possible call date.
Typically a bond issuer will call a bond only if it will result in a financial gain. For example, if the interest rate drops below a coupon rate, the issuer may decide to recall the bond to borrow funds at a lower rate. This situation is similar to when interest rates drop and homeowners refinance their home loans.
For investors that use callable bonds for income, yield to call is significant. Suppose the issuer decides to call the bond when the interest rates are lower than when the investor purchases it. If an investor decides to reinvest their payout, they may have a tough time finding a comparable bond that offers the yield they need to support their lifestyle. They may feel it necessary to take on more risk, looking to high-yield bonds.
💡 Quick Tip: It’s smart to invest in a range of assets so that you’re not overly reliant on any one company or market to do well. For example, by investing in different sectors you can add diversification to your portfolio, which may help mitigate some risk factors over time.
Yield to Maturity vs Coupon Rate
While a bond’s coupon rate is another important piece of information that investors need to keep in mind, it’s not the same as yield to maturity. The coupon rate tells investors the annual amount of interest that a bond’s owner is set to receive — the two may be the same when a bond is initially purchased, but will likely diverge over time due to changing economic and market conditions.
Limitations of Yield to Maturity
The yield to maturity calculation does have limitations.
Taxes
It’s important to note that YTM calculations exclude taxes. While some bonds, like municipal bonds and U.S. Treasury bonds, may be tax exempt on a federal and state level, most other bonds are taxable. In some cases, a tax-exempt bond may have a lower interest rate but ultimately offer a higher yield once taxes are factored in.
As an investor, it can be especially helpful to consider the after-tax yield rate of return. For example, suppose an investor in the 35% federal tax bracket who doesn’t pay state income taxes is considering investing in either Bond X or Bond Y. Bond X is a tax-exempt bond and pays a 4% interest rate, while Bond Y is taxable and pays 6% interest.
While the 4% yield for Bond X remains the same, the after-tax yield for Bond Y is 3.8%. While it seemed like the less lucrative of the two options up front, Bond X should ultimately yield a higher return after taxes.
Presuppositions
Another YTM limitation is that it makes assumptions about the future that may not necessarily come to fruition. Specifically, it assumes that a bondholder will hang on to the bond until its maturity date, which may or may not actually happen. It also assumes that profits from the investment will be reinvested in a uniform manner — again, that may or may not be the case.
The Takeaway
Using the yield to maturity formula can help investors compare bond options with different coupon and maturity rates, market and par values, and determine which one offers the potential for a higher yield. But calculating the YTM is not an exact science, especially when you’re gauging the return on a callable bond, say, or adding the impact of taxes to the mix.
YTM is just one tool investors can use to determine which bond may best serve their financial needs and goals. One alternative to choosing individual bonds is to invest in bond mutual funds or bond exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Investors can also speak with a financial professional for guidance.
Invest in what matters most to you with SoFi Active Invest. In a self-directed account provided by SoFi Securities, you can trade stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), mutual funds, alternative funds, options, and more — all while paying $0 commission on every trade. Other fees may apply. Whether you want to trade after-hours or manage your portfolio using real-time stock insights and analyst ratings, you can invest your way in SoFi's easy-to-use mobile app.
Opening and funding an Active Invest account gives you the opportunity to get up to $1,000 in the stock of your choice.¹
FAQ
What is a bond’s yield to maturity (YTM)?
What is a bond’s yield to maturity (YTM)?
A bond’s yield to maturity is the total return an investor can anticipate receiving if the bond is held to its maturity date. YTM calculations assume that all interest payments will be made by the issuer and reinvested by the bondholder at a constant rate of interest.
What is the difference between a bond’s coupon rate and its YTM?
A bond’s coupon, or interest, rate is fixed from the moment an investor buys it. However, the same bond’s YTM can fluctuate over time depending on the price paid for it and other interest prices available on the market. If YTM is lower than the coupon rate, it may indicate that the bond is being sold at a premium to its face value. If it’s lower, it may be that the bond is priced at a discount to face value.
What is yield to maturity and how is it calculated?
Yield to maturity refers to the total return an investor can expect or anticipate from a bond if they hold it to maturity. It’s calculated using variables including the time to maturity, a bond’s face value, its current price, and its coupon rate.
Why is yield to maturity important?
The yield to maturity formula can give investors an idea of what they can expect in terms of returns from their bond holdings. But again, there are some assumptions the calculation takes into account, so an investor’s mileage may vary.
Is a higher YTM better?
A higher YTM may be better under certain circumstances. For example, since a higher YTM may indicate a bond is being sold for less than its face value, it may represent a valuable opportunity to invest. However, if the bond is discounted because the company that offered it is in trouble or interest rates offered by other investments are more appealing, then a high YTM might not be such a good thing. Investors must research investments carefully and understand the full story before they buy.
INVESTMENTS ARE NOT FDIC INSURED • ARE NOT BANK GUARANTEED • MAY LOSE VALUE
For disclosures on SoFi Invest platforms visit SoFi.com/legal. For a full listing of the fees associated with Sofi Invest please view our fee schedule.
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
¹Probability of Member receiving $1,000 is a probability of 0.026%; If you don’t make a selection in 45 days, you’ll no longer qualify for the promo. Customer must fund their account with a minimum of $50.00 to qualify. Probability percentage is subject to decrease. See full terms and conditions.
SOIN0623030 Read more




