When Can I Retire Calculator
Table of Contents
When it comes to figuring out when you can retire, there are a number of factors to consider, including Social Security, other sources of income like a pension, and expenses such as health care costs.
Thankfully, there’s retirement calculators for figuring out these costs, which might help you plan for the future. But first, to decide when you can retire, determine at what age you want to retire and then see how that decision affects your finances.
Key Points
• Factors to consider when deciding when to retire include Social Security benefits, other sources of income, and expenses like health care costs.
• The full retirement age for Social Security benefits varies based on birth year.
• Early retirement can result in reduced Social Security benefits, while delaying retirement can increase monthly benefits.
• Different retirement accounts, such as Roth IRAs and traditional IRAs, have specific rules for withdrawals.
• Other sources of retirement income to consider include part-time work, pensions, inheritance, and rental income.
When Can You Get Full Social Security Benefits?
As you consider when to apply for Social Security, you’ll want to understand at what age the government allows people to retire with full Social Security benefits. Not only that, at what age can people start withdrawing from their retirement accounts without facing penalties? For Social Security, the rules are based on your birth year.
The Social Security Administration (SSA) has a retirement age calculator. For example, people born between 1943 and 1954 could retire with full Social Security benefits at age 66.
Meanwhile, those born in 1955 could retire at age 66 and two months, and those born in 1956 could retire at age 66 and four months. Those born in or after 1960 can retire at age 67 to receive full benefits. This can help with your retirement planning.
When you plan to retire is important as you consider your Social Security benefits. What you can collect at full retirement age is different from what you can collect if you retire early or late.
In a 2024 SoFi Retirement Survey, two out of three respondents say they are somewhat or very confident they can retire on time: 70% are hoping to leave the workforce at age 60 or older. Others hope to retire early —17% would like to retire between the ages of 50 and 59.
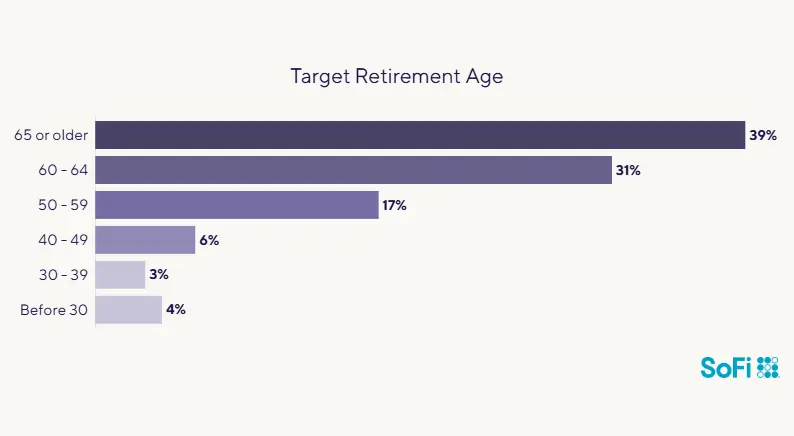
Source: SoFi’s 2024 Retirement Survey
Social Security Early Retirement
A recipient’s benefits will be permanently reduced if they retire before full retirement age. That’s because the earlier a person retires, the less they’ll receive in Social Security.
Let’s use Jane Doe as an example and say she was born in 1960, so full retirement age is 67. If she retires at age 66, she’ll receive 93.3% of Social Security benefits; at age 65 will get Jane 86.7%. If she retires on her 62nd birthday — the earliest she can receive Social Security — she’ll only receive 70% of earnings.
Here’s a retirement planner table for those born in 1960, which shows how one’s benefits will be reduced with early retirement.

Source: Social Security Administration
Social Security Late Retirement
If a person wants to keep working until after full retirement age, they could earn greater monthly benefits. This is helpful to know when choosing your retirement date.
For example, if the magic retirement number is 66 years but retirement is pushed back to 66 and one month, then Social Security benefits rise to 100.7% per month. So if your monthly benefit was supposed to be $1,000, but you wait until 66 years and one month, then your monthly allotment would increase to $1,007.
If retirement is pushed back to age 70, earnings go up to 132% of monthly benefits. But no need to calculate further: Social Security benefits stop increasing once a person reaches age 70. Here is a SSA table on delayed retirement .
Other Retirement Income to Consider
In retirement, you may have other income sources that can help you support your lifestyle and pay the bills. These might include:
Part-Time Work
Working after retirement by getting a part-time job, especially if it’s one you enjoy, could help cover your retirement expenses. And as long as you have reached your full retirement age (which is based on your year of birth, as noted above), your Social Security benefits will not be reduced, no matter what your earnings are.
However, if you retire early, you need to earn under an annual limit, which is $23,400 in 2025, and $24,480 in 2026, to keep your full benefits. If you earn more than that, you’ll lose $1 in Social Security benefits for every $2 you earn over the limit.
Pension
A pension plan, also sometimes known as a defined benefits plan, from your employer is usually based on how long you worked at your company, how much you earned, and when you stopped working. You’ll need to be fully vested, which typically means working at the company for five years, to collect the entire pension. Check with the HR rep at your company to get the full details about your pension.
A pension generally gives you a set monthly sum for life or a lump sum payment when you retire.
Inheritance
If you inherit money from a relative, these funds could also help you pay for your retirement. And fortunately, receiving an inheritance won’t affect your Social Security benefits, because Social Security is based on money you earn.
Rental Income
Another potential money-earning idea: You could rent out a home you own, or rent out just the upper floors of the house you live in, for some extra income in retirement. Like an inheritance, rental income will generally not affect your Social Security benefits.
Major Expenses in Retirement
It’s important to draw up a budget for retirement to help determine how much money you might need. The amount may be higher than you realize — which is one of the reasons it’s beneficial to start saving early. In SoFi’s retirement survey, more than half of respondents (51%) say they started saving before age 35.
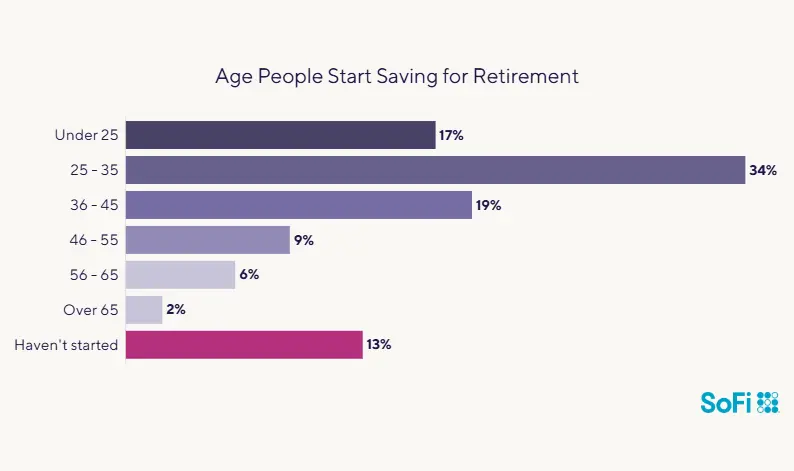
Source: SoFi’s 2024 Retirement Survey
As you put together your retirement budget, these are some of the major expenses retirees commonly face.
Healthcare
For most people, health care costs increase as they get older, as medical problems can become more serious or pervasive. According to Fidelity, based on 2024 numbers, the average amount that a couple who are both age 65 will spend on health care during their first year of retirement is $12,800.
Housing
Your mortgage, home insurance, and the costs of maintaining your house can be a significant monthly and yearly expense. In fact, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ 2023 Consumer Expenditures report, Americans aged 65 and older spent an average of $21,445 on housing in 2023.
Travel
If you’re planning to take trips in retirement, or even just drive to visit family, transportation costs can quickly add up. The Bureau of Labor Statistics Consumer Expenditures report found that in 2023, people over age 65 averaged about $9,033 in transportation costs a year, including vehicles, maintenance, gas, and insurance.
💡 Quick Tip: You can’t just sit on the money you save in a traditional IRA account forever. The government requires withdrawals each year, starting at age 73 (for those born in 1950 or later). These are called required minimum distributions or RMDs.
When Can You Withdraw From Retirement Accounts?
Now that you have a sense of your expenses in retirement, let’s look at retirement accounts. Each type of account has different rules about when money can be taken out.
If a Roth IRA account has existed for at least five years, withdrawals can generally be taken from the account after age 59 ½ without consequences. These are known as qualified withdrawals. Taking out money earlier or withdrawing money from a Roth IRA that’s been open for fewer than five years could result in paying penalties and taxes.
There is a little wiggle room. Contributions (but not earnings) can be withdrawn at any time without penalty, no matter the age of the account holder or the age of the account.
Roth IRA withdrawal rules also have some exceptions. Qualified withdrawals may be made from an account that’s been open at least five years for the purchase of a first home (up to a $10,000 lifetime limit), due to a disability, or after the account holder’s death to be paid to their estate or a beneficiary.
People with a traditional IRA can make withdrawals after age 59 ½ without being penalized. The government will charge a 10% penalty on withdrawals before age 59 ½. There are some exceptions, such as the purchase of a first home (up to a $10,000 lifetime limit), some medical and educational expenses, disability, and death.
People with 401(k)s can make withdrawals after age 59 ½ without paying a 10% penalty. Again, there are some exceptions. For example, an individual can generally retire at age 55 and make withdrawals without penalty. There are also exceptions for those under age 59 ½ for hardship withdrawals, disability, and death, among others.
It’s important to be aware that with a traditional IRA and a 401(k), individuals must start making required minimum distributions (RMDs) by age 73 or face a penalty.
Test your understanding of what you just read.
The Takeaway
Deciding at what age to retire is a personal choice. However, by planning ahead for some common expenses, and understanding the age at which you can get full Social Security benefits, you can use a retirement calculator formula to estimate how much money you’ll need each year to live on. And you can supplement your Social Security benefits with other forms of income and by making smart decisions about savings and investments.
Prepare for your retirement with an individual retirement account (IRA). It’s easy to get started when you open a traditional or Roth IRA with SoFi. Whether you prefer a hands-on self-directed IRA through SoFi Securities or an automated robo IRA with SoFi Wealth, you can build a portfolio to help support your long-term goals while gaining access to tax-advantaged savings strategies.
FAQ
How do I calculate my retirement age?
To calculate your full retirement age, which is the age you can receive your full retirement benefits, you can use the Social Security administration’s retirement age calculator . Essentially, if you were born in 1960 or later, your full retirement age is 67. For those born between 1954 and 1959, the full retirement age is between 66 and 67, depending exactly how old they are when they retire (such as age 66 and two months). And for those born between 1943 and 1954, full retirement age is 66.
The earlier you retire before your full retirement age, the less you’ll receive in benefits. Conversely, the longer you keep working, up to age 70, the more you can receive.
Can you legally retire before 55?
Yes, you can legally retire before age 55. However, your Social Security benefits typically won’t kick in until age 62. And even then, because you’ll be tapping into those benefits before your full retirement age of 66 or 67, you’ll get a reduced amount.
The rule of 55 generally allows you to withdraw funds from a 401(k) or 403(b) at age 55 without paying a penalty. That may be something to look into if you’re planning to retire early.
Can you retire after 20 years of work?
In some lines of work, you can retire after 20 years on the job and likely get a pension. This includes those in the military, firefighters, police officers, and certain government employees.
That said, anyone in any industry can retire at any time. However, Social Security benefits don’t typically begin until age 62.
INVESTMENTS ARE NOT FDIC INSURED • ARE NOT BANK GUARANTEED • MAY LOSE VALUE
For disclosures on SoFi Invest platforms visit SoFi.com/legal. For a full listing of the fees associated with Sofi Invest please view our fee schedule.
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
Disclaimer: The projections or other information regarding the likelihood of various investment outcomes are hypothetical in nature, do not reflect actual investment results, and are not guarantees of future results.
Third-Party Brand Mentions: No brands, products, or companies mentioned are affiliated with SoFi, nor do they endorse or sponsor this article. Third-party trademarks referenced herein are property of their respective owners.
Third Party Trademarks: Certified Financial Planner Board of Standards Center for Financial Planning, Inc. owns and licenses the certification marks CFP®, CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER®
External Websites: The information and analysis provided through hyperlinks to third-party websites, while believed to be accurate, cannot be guaranteed by SoFi. Links are provided for informational purposes and should not be viewed as an endorsement.
SOIN-Q325-038
CN-Q425-3236452-125




