How to Stop Overspending Money
Table of Contents
If you feel that, despite your best intentions, your hard-earned money gets frittered away, you may need to curb your spending.
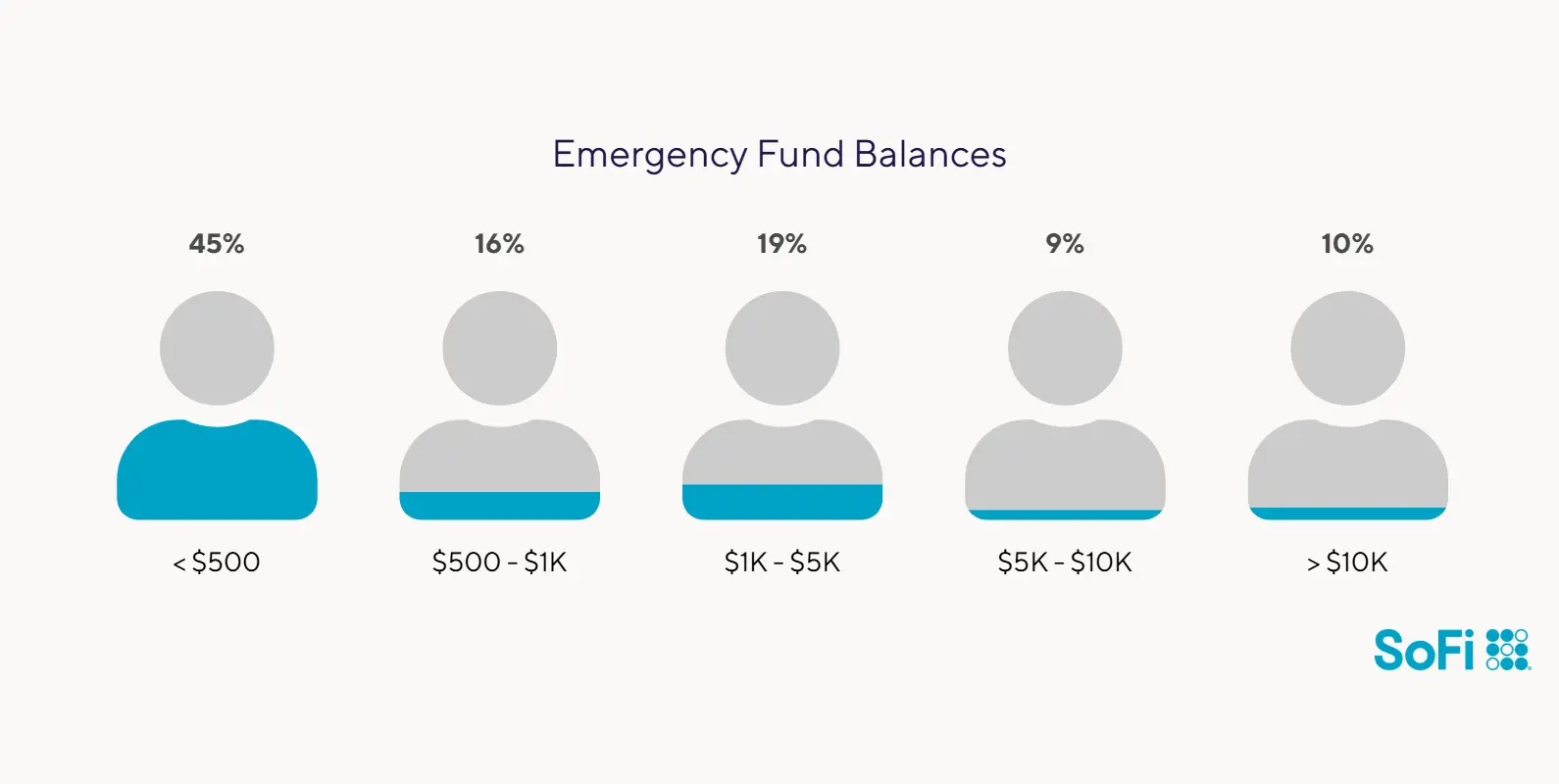
Sure, shopping and dining out are part of life, but the convenience of tapping and swiping can make it easy to overdo it. And all the tempting things you see on social media can lead to less than mindful buying, not to mention credit card debt. In fact, the average American currently has $6,730 in high-interest credit card debt, according to Experian®’s latest research, and some of that could be due to overspending.
Read on to learn more about what can cause you to overspend, plus tactics that can help you better control your spending.
Key Points
• To stop spending money, individuals should identify their spending triggers and understand the emotions behind their spending habits.
• Creating a budget and tracking expenses helps individuals gain awareness of where their money is going.
• Practicing delayed gratification by waiting before making non-essential purchases can curb spending.
• Finding alternative activities or hobbies that bring joy without requiring excessive spending is beneficial.
• Understanding how FOMO, lifestyle creep, and social media impact your financial habits can help you rethink spending and save more.
12 Ways to Stop Overspending
If you find yourself being a bit too freewheeling with your spending, try some tactics to help you cut back.
1. Mapping Out a Budget
Without a budget, you can spend money mindlessly, without thinking much about it. To create a budget and learn how to be better with money, check your income and track your current spending patterns from bank and credit card statements. You can also use a free tool to track your spending, which makes the process even easier. You can start by seeing what your financial institution offers.
Identify essential expenses vs. non-essential ones. Necessary spending includes such items as housing, groceries, utilities, health care costs, and transportation. Non-essential costs are things like eating out, leisure travel, and entertainment — and they can add up to a lot of money over a month.
Once you see how much you spend in each expense category, it may be easier to reduce spending. Experiment with different budget methods to find the right fit.
Recommended: 50/30/20 Budget Calculator
2. Calculating Hourly Earnings
A night out may not seem like a huge splurge in the moment — especially when compared to your total earnings for the month. But, that same expense can quickly appear more significant when you tabulate how many hours of work are needed to pay for it.
To try this approach, figure out your hourly pay: Divide your after-tax pay by the number of hours worked. If you get paid twice a month and work a 40-hour week, divide your total earnings by 80 (two weeks times 40 hours). Then use that insight:
• For instance, a birthday dinner and drinks with friends that costs $200 would translate to four hours of work if you earn $50 per hour.
Whether that spend feels worth it is a personal decision, but this process can nudge you to consider carefully to make sure the expense feels worth it.
3. Understanding What Triggers Spending
Whether it’s the gourmet food section at the grocery store, the Instagram influencer with the covetable closet of clothes, or that friend who drops big bucks on concert tickets, for all of us, the urge to spend can be triggered by emotions and outside influences.
Even the physical shopping environment — in-store displays, prominent markdown messaging, and subtler cues like store layout — can trigger people to overspend. When figuring out how to stop spending money, it can be key to understand which emotional or psychological cues make you take out your wallet and short-circuit their impact on you.
💡 Quick Tip: Want to save more, spend smarter? Let your bank manage the basics. It’s surprisingly easy, and secure, when you open an online bank account.
4. Shopping with a Plan
Of course you can’t always avoid spending triggers. We all have to shop sometimes. But here’s how to stop overspending: Create a shopping list, and stick to it. That’s one way to spend wisely.
For example, going grocery shopping may be easiest to do right after work. But that time of day may also coincide with when you’re ravenous. Hungry shoppers, research shows, tend to buy more non-essential items.
Increase your savings
with a limited-time APY boost.*
5. Finding It Cheaper
There are times when you’ll choose to spend money on specific purchases. Comparison shopping may help you cut back on expenses since you may be able to find the item cheaper elsewhere. Try these tips, too:
• Try couponing and discount codes. There are many sites that can help, such as Coupons.com and Retailmenot.com.
• Join a warehouse or wholesale club. These stores can be cheaper than your local supermarket. Are the quantities too big for your household? Share them with friends and split the cost.
• Shop where you get rewards that lower your costs. Loyalty can pay off.
6. The 30 Day Rule
Want another way to avoid overspending? Before you purchase something, take some time to think it over, rather than giving in to impulse buying.
Studies show that activities that provide instant gratification, such as impulse shopping, activate feel-good chemicals in the brain, according to the Cleveland Clinic. But that purchase could come at the expense of your financial standing. How to avoid that:
• If you see an item of significant expense that triggers a “gotta have it” feeling, put a note in your calendar for 30 days later. Write down the item, the price, and where you saw it.
• When that date rolls around, if you still feel you must have the object of your affection, you can decide to get it. But there’s a very good chance that your sense of urgency will have passed. That can be a way to stop spending money.
7. A No-Spend Challenge
You can gamify your spending to help you save. Try a no-spend challenge; you may want to have a friend or family member join you to make it more fun and help you stay accountable.
In a no-spend challenge, you typically pick a period of time during which you will only buy essentials. One popular option is a No-Spend September. Or you might declare that you won’t buy any fancy coffees for a week and put the money saved toward debt. Then, the next month, you could not buy any personal care items that are luxuries rather than necessities.
Recommended: 15 Creative Ways to Save Money
8. Using Cash Instead of Credit
When you swipe or tap a credit card, it can feel almost as if you aren’t spending money at all. But of course you are, and what you spend will accrue high interest if you don’t pay it off promptly and in full.
However, if you instead commit to using cash or a debit card to pay for purchases as often as possible, you can only really spend what you have. This can help you be more in touch with your money and avoid splashing out on random unplanned purchases, whether that’s a daily fancy iced coffee or a new wristwatch you stumble upon at the mall. (Of course, sometimes life happens, you make an error, and spend more than you have. That’s where overdraft protection can come in handy.)
9. Setting Up Automatic Savings Transfers
Many people overspend because they see money in their checking account, feel flush, and go shopping. But then, when it’s time to fund your savings (whether for summer vacation or the down payment on the house), you don’t have enough cash.
That’s why the habit of paying yourself first is a good one, and automating savings by setting up recurring transfers from your checking account to savings can be valuable. It can be wise to have an amount (20% of your paycheck is recommended by many financial experts, but even $25 is a start) whisked out right after your paycheck hits.
This can help you save regularly and fund your financial goals; you can even set up separate savings vaults for different goals.
10. Focus on Value vs Price
Here’s a smart way to think about your spending: Price is what you pay, and value is what you get. So if you spend $300 on a pair of shoes but you don’t wear them often or they fall apart quickly, you haven’t gotten good value for the price.
This is not to say that higher-priced items are never worth the cost. If you pay $300 for a pair of shoes that are top quality, last for years, and can be worn often, you’ve gotten great value. By thinking of value instead of price, you can avoid overspending, whether that means paying too much for an item that isn’t worth it or else buying a bargain-priced product that doesn’t deliver.
11. Reduce Dining Out
Dining out can be a fun way to socialize and enjoy food you couldn’t (or wouldn’t) make at home. But the cost can really add up and empty out your checking account. The average monthly spend dining at restaurants in 2024 was $191 vs. $166 in 2023, according to data from US Foods.
To save some cash, consider meeting friends for, say, a walk in the park or a free day at a local museum instead of a pricey brunch out. Or you might create a recipe club with friends in which you try cooking new dishes together. To save money when dining out, try tricks like skipping high-priced cocktails or splitting a few appetizers instead of ordering main courses.
12. Cancel Unnecessary Subscriptions
Comb through your credit card charges carefully, and you may discover that you are paying every month for subscriptions that you’ve forgotten about or aren’t getting good value from. That language app you signed up for before last year’s trip to Spain may still be charging you even though you haven’t opened it in months. You could live without it and keep that money. Or you might save on streaming services because you realize you actually aren’t watching one or two and can cancel them.
Recommended: How to Make Money Fast
5 Factors That Contribute to Your Spending Problem
As you work to stop overspending money, you may want to consider and avoid some of the things that can trigger you to dole out too much cash.
1. Social Media
As you scroll on Instagram, TikTok, and other platforms, you are likely to be exposed to dozens of influencers and offers that can encourage you to buy things you never previously knew about or wanted. Recognize that social media can encourage you to buy items (from kitchen gadgets to gummy candy) that you would never otherwise buy just because you’re a captive audience for clever marketing.
One way to fight back? It may be helpful not to link your credit card to your social media accounts to minimize the possibility of overspending.
2. Emails and Text Messages
Here’s another way your digital life can contribute to overspending: If you get emails or text messages heralding new products, sales, and other offers, it can trigger you to buy.
For example, if your favorite home design retailer sends you a message saying their most popular throw pillows are almost sold out, that may get you to buy. Unsubscribing from these marketing messages can be a budget-wise move.
3. Retail Therapy
Many of us shop as a pick-me-up. If you’re having a bad day at work, had a fight with your significant other, or are stressed about almost anything, hitting some stores can be a welcome distraction. However, this can also lead you to buy things that you neither need nor craved before you set foot inside the shop.
Recognizing what triggers retail therapy can help you break a bad spending habit. Or you can try the tactic of leaving your credit cards at home when you go browsing at boutiques.
4. FOMO
FOMO stands for “fear of missing out,” and it can drive a lot of impulse purchases. If your friend says you must try a pricey new restaurant in your neighborhood or your coworker suggests a life-changing hairstylist, you might feel as if, yes, you must spend money on these things. It can make you feel as if you are part of the in-crowd or “keeping up with the Joneses.”
Understanding this FOMO spending dynamic can be a major step toward stopping this kind of overspending.
5. Lifestyle Creep
Lifestyle creep occurs when, as you earn more, you spend more. Many people think that getting, say, a 10% raise is license to go spend 10% more. However, this can just keep your finances at a baseline level rather than helping you build wealth and reach longer-term goals.
As your income climbs, it can be wiser to raise your debt payments or put more in a high-yield online savings account rather than heading to the mall to celebrate.
The Takeaway
While it’s not possible to stop spending money altogether, adopting a few smart habits — such as budgeting, understanding your spending triggers, and shopping with a list — could help you take control of your money and spend less.
The right banking partner can help with budgeting, tracking your spending, and putting your money to work for you.
Interested in opening an online bank account? When you sign up for a SoFi Checking and Savings account with eligible direct deposit, you’ll get a competitive annual percentage yield (APY), pay zero account fees, and enjoy an array of rewards, such as access to the Allpoint Network of 55,000+ fee-free ATMs globally. Qualifying accounts can even access their paycheck up to two days early.
FAQ
What is it called when you can’t stop spending money?
There are various terms used to describe the issue of spending too much, such as compulsive shopping, impulsive shopping, shopping addiction, and pathological buying.
Is overspending a mental disorder?
Sometimes called money dysmorphia or money disorder, overspending may be considered a psychological disorder. It involves a person being preoccupied with money, spending it, and financial status. It can trigger feelings of anxiety and inadequacy. In addition, compulsive shopping can be considered a form of obsessive-compulsive or impulse-control disorder. Working with a qualified therapist can be helpful in managing the psychological reasons for overspending.
How much is too much spending?
There is no set amount that equals too much spending. Rather, it occurs when spending negatively impacts your financial and personal life. If you can’t stick to a budget, are burdened by debt, or find that your preoccupation with shopping interferes with your work or relationships, then your spending could be excessive.
How do I stop the cycle of overspending?
You can stop the cycle of overspending in a variety of ways, including creating and sticking to a budget, planning your purchases (whether a big-ticket item or just weekly groceries), using cash, and going on a spending freeze.
What is the root cause of overspending?
Overspending has various causes. It could be due to boredom, lifestyle creep, FOMO (fear of missing out), and wanting to reward oneself or boost one’s mood, among other reasons.
SoFi Checking and Savings is offered through SoFi Bank, N.A. Member FDIC. The SoFi® Bank Debit Mastercard® is issued by SoFi Bank, N.A., pursuant to license by Mastercard International Incorporated and can be used everywhere Mastercard is accepted. Mastercard is a registered trademark, and the circles design is a trademark of Mastercard International Incorporated.
Annual percentage yield (APY) is variable and subject to change at any time. Rates are current as of 12/23/25. There is no minimum balance requirement. Fees may reduce earnings. Additional rates and information can be found at https://www.sofi.com/legal/banking-rate-sheet
Eligible Direct Deposit means a recurring deposit of regular income to an account holder’s SoFi Checking or Savings account, including payroll, pension, or government benefit payments (e.g., Social Security), made by the account holder’s employer, payroll or benefits provider or government agency (“Eligible Direct Deposit”) via the Automated Clearing House (“ACH”) Network every 31 calendar days.
Although we do our best to recognize all Eligible Direct Deposits, a small number of employers, payroll providers, benefits providers, or government agencies do not designate payments as direct deposit. To ensure you're earning the APY for account holders with Eligible Direct Deposit, we encourage you to check your APY Details page the day after your Eligible Direct Deposit posts to your SoFi account. If your APY is not showing as the APY for account holders with Eligible Direct Deposit, contact us at 855-456-7634 with the details of your Eligible Direct Deposit. As long as SoFi Bank can validate those details, you will start earning the APY for account holders with Eligible Direct Deposit from the date you contact SoFi for the next 31 calendar days. You will also be eligible for the APY for account holders with Eligible Direct Deposit on future Eligible Direct Deposits, as long as SoFi Bank can validate them.
Deposits that are not from an employer, payroll, or benefits provider or government agency, including but not limited to check deposits, peer-to-peer transfers (e.g., transfers from PayPal, Venmo, Wise, etc.), merchant transactions (e.g., transactions from PayPal, Stripe, Square, etc.), and bank ACH funds transfers and wire transfers from external accounts, or are non-recurring in nature (e.g., IRS tax refunds), do not constitute Eligible Direct Deposit activity. There is no minimum Eligible Direct Deposit amount required to qualify for the stated interest rate. SoFi Bank shall, in its sole discretion, assess each account holder's Eligible Direct Deposit activity to determine the applicability of rates and may request additional documentation for verification of eligibility.
See additional details at https://www.sofi.com/legal/banking-rate-sheet.
*Awards or rankings from NerdWallet are not indicative of future success or results. This award and its ratings are independently determined and awarded by their respective publications.
We do not charge any account, service or maintenance fees for SoFi Checking and Savings. We do charge a transaction fee to process each outgoing wire transfer. SoFi does not charge a fee for incoming wire transfers, however the sending bank may charge a fee. Our fee policy is subject to change at any time. See the SoFi Bank Fee Sheet for details at sofi.com/legal/banking-fees/.
SoFi Relay offers users the ability to connect both SoFi accounts and external accounts using Plaid, Inc.’s service. When you use the service to connect an account, you authorize SoFi to obtain account information from any external accounts as set forth in SoFi’s Terms of Use. Based on your consent SoFi will also automatically provide some financial data received from the credit bureau for your visibility, without the need of you connecting additional accounts. SoFi assumes no responsibility for the timeliness, accuracy, deletion, non-delivery or failure to store any user data, loss of user data, communications, or personalization settings. You shall confirm the accuracy of Plaid data through sources independent of SoFi. The credit score is a VantageScore® based on TransUnion® (the “Processing Agent”) data.
Financial Tips & Strategies: The tips provided on this website are of a general nature and do not take into account your specific objectives, financial situation, and needs. You should always consider their appropriateness given your own circumstances.
Third-Party Brand Mentions: No brands, products, or companies mentioned are affiliated with SoFi, nor do they endorse or sponsor this article. Third-party trademarks referenced herein are property of their respective owners.
Third Party Trademarks: Certified Financial Planner Board of Standards Center for Financial Planning, Inc. owns and licenses the certification marks CFP®, CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER®
SOBNK-Q225-109
Read more